3D 모델을 로딩하는 또 다른 강좌를 진행하는 이유는 애니메이션 강좌(다음 강좌)를 하고싶기 때문입니다. obj 포맷은 애니메이션을 저장하지 않기때문에 (여러분이 애니메이션의 각 프레임마다 따로 분리된 모델을 저장하는 키프레임 애니메이션을 위해 obj 포맷을 사용해도 됩니다. 많은 장점이 있습니다. 모든 프레임마다 정확히 계획한대로 보이고 모델사이 스위치하는것도 매우 빨라서 성능상으로도 좋습니다. 하지만 단점으로 완전히 정적이고 메모리를 많이 차지합니다.) 이를 수행하는 다른 포맷을 정해야 했습니다. 조사 끝에 이번 강좌를 위한 잘 만든 포맷을 알아냈다고 생각합니다. 바로 MD5 입니다.
여러분은 MD5 포맷에 관해 모를 수 있는데 바로 Doom 3에 사용된 포맷입니다. MD5 포맷은 정점 위치를 정의하기위해 뼈대(관절) 구조를 사용하는데 이게 제가 이 포맷을 선택한 이유입니다. MD5 포맷은 2개의 파일로 구성되는데 "md5mesh"와 "md5anim"입니다. 이 파일들은 아스키값으로 저장되어 있어 읽기 매우 쉽습니다. "md5mesh"은 이번 강좌에서 기하, 물질같은 모델 정보를 저장하는데 초점에 맞출 것이고 "md5anim"은 다음 강좌에서 모델의 애니메이션을 저장하는데 초점을 맞출 것입니다.
진행하기 전에 제가 이 강좌를 만들때 참고한 두 기사를 언급하고 싶습니다. 여기랑 여기입니다.
Skeletal Animation (Brief Intro.)
뼈대 애니메이션은 키프레임 애니메이션(애니메이션의 각 프레임에 대해 모델의 분리된 버전을 저장한다)의 대책입니다. 뼈대 애니메이션은 뼈대의 유형을 정의하여 각 모델 정점들에 뼈 혹은 관절에 대한 weight를 주는 곳입니다. 각 정점은 한 개 혹은 그 이상의 weight를 갖습니다. weight는 관절 또는 뼈에 대한 위치와 가중치를 정의합니다. 가중치는 특정 정점 이상을 갖는 weight를 어떻게 조절할지를 결정합니다. 각 정점은 한 개 이상의 weight를 포함하기 때문입니다. 한 정점의 weight의 가중치의 총합은 반드시 "1"이 되야 합니다.
2가지 다른 유형의 뼈대 애니메이션 구조가 있습니다. 하나는 관절을 사용하고 하나는 실제 뼈와 매우 유사한 시스템을 사용합니다.
우리가 사용할 관절 시스템은 과절의 위치와 관절의 방향, 부모 관절을 정의합니다. 모든 관절은 단 하나(루트 관절)을 제외하고 반드시 부모 관절을 가지며 루트 관절은 계층의 가장 상위에 있고 부모 관절을 -1로 설정합니다. 부모 관절이 회전되거나 움직이면 자식 관절도 똑같이 적용됩니다. 예를들어 만약 여러분이 사람의 위쪽 팔을 움직이면 아랫쪽 팔, 손 그리고 손가락들도 같이 움직입니다. 자식 관절은 항상 부모 관절에 붙어져있으며 관절을 분리하는 것은 불가능하며 모델을 폭발시키고 싶어도 안됩니다. 만약 총에 맞은 후 머리를 떨어뜨리고 싶으면 관절의 방향을 0으로 설정해야하며 그러면 머리가 날라가는 것처럼 보일 겁니다.
다른 뼈 시스템은 뼈에대해 위치 두개를 명시하는데 하나는 뼈의 끝을 하나는 부모것을 명시합니다. 이 시스템은 폭발하는 모델에 쓰면 좋은데 뼈들이 분리가 가능하기 때문입니다.
비록 이 사이트는 OpenGL로 되어있지만 애니메이션에 대한 좋은 기사입니다. (사이트 링크를 따라가면 도메인 만료로 뜨지 않아서 안썼습니다.)
The MD5 Format
위에서 설명한것 처럼 MD5 포맷은 두개의 파일을 포함합니다. 이번 강좌에서는 모델의 bind-pose를 저장하는 md5mesh만 사용할 것입니다. bind-pose는 모델의 기본 위치입니다. 다음 강좌에서는 여전히 서있지 않게 하도록 모델을 어떻게 움직이는지(animate) 배울것입니다.
또 포맷파일은 아스키값으로 되어있다고 언급했었는데 그래서 읽기가 쉽습니다. 모든 의미있는 줄은 해당 줄이 포함하는 것을 설명하는 문자열로 시작할것입니다. (혹은 많은 경우 그 뒤 라인도 포함하여) 다음 여러 섹션들은 라인이나 라인들을 정의하는 이름이 붙은 각 라인이 무엇을 위한것인지 설명할 것입니다.
"MD5Version"
이 문자열은 파일의 버전을 설명하는 숫자입니다. 우리의 로더는 버전 10에 대해 맞추어 제작되었니다. (로더에서 실제 버전 확인을 하지는 않습니다) 여러분이 다른 버전에 대한 정보를 알 수 있습니다. 뭐 제가 다운받은 모든 md5 모델은(사실 많지는 않아요) 전부 버전 10이었지만..
"commandline"
이 라인은 신경 쓰실것 없습니다. 데헷
"numJoints"
이 라인은 모델에서 관절의 개수를 가집니다.
"numMeshes"
모델에서 mesh(서브셋"들" 이라 부를; mesh내에 많은 서브셋(shader, vert 등등)이 있음)의 개수를 나타냅니다. 각 mesh(or 서브셋)는 정점(위치 x, 위치는 weight를 이용하여 계산될 것입니다. 법선도 마찬가지), 삼각형, weight를 정의합니다.
"joints"
관절 설명의 시작 부분입니다. 관절 설명은 다음 라인에서 시작하여("joints {" 뒤부터) 닫는 괄호("}")를 만나는 라인까지 입니다.
"joints {" 뒤 각 라인은 새로운 관절입니다. 이 각 라인들은 안에 큰따옴표로 시작하며 따옴표 사이는 관절의 이름입니다. 관절 이름 바로 다음은 해당 관절의 ID 번호입니다. ID 번호 "-1"을 가진 관절은 루트 관절입니다. ID 다음은 관절의 위치를 나타내는 3D 벡터(괄호 사이)입니다. 그 다음 또 다른 3D 벡터(역시 괄호 사이)는 관절 "bind-pose" 방향을 나타냅니다. 관절 방향을 파일에서는 3D 벡터로 저장되지만 실제로는 사원수로 사용됩니다. (혹은 4D 벡터) 사원수는 밑에서 간단하게 설명할 것입니다.
"mesh"
이 문자열은 mesh 또는 subset의 시작입니다. 열고 닫는 괄호({ ...}) 사이 모든 것은 이 특정 subset을 정의합니다. "md5mesh" 파일은 관절에 대한 하나의 섹션만 가지지만 각 mesh 또는 subset에 대한 섹션은 하나 이상 가질 수 있습니다. 다행히도 파일의 헤더가 subset의 개수를 정의하기 때문에 마지막 섹션을 읽었을때 알 수 있을 것입니다.
"shader"
첫번째 중요 라인 (가끔 "mesh {" 라인 뒤에 바로 subset의 이름을 나타내는 주석이 달려있습니다.)은 shader입니다. 이 라인은 모델이 사용할 재질이나 텍스쳐의 이름을 가집니다. (문자열은 큰따옴표안에 있어서 문자열을 읽으신 후 따옴표를 제거하셔야 할 것입니다.) MD5 포맷은 OBJ 포맷처럼 material library 파일을 포함하지 않기 떄문에 여러분의 모델에 재질을 사용하고 싶으면 직접 여러분만의 material library를 만드셔야 합니다. (기본으로 적어도 제 3ds max 익스포터에서 텍스쳐 이름 대신 재질 이름이 사용됩니다.) 그와 다르게 간단하게 하기 위해 각 subset에 대한 재질 이름을 각 mesh에 대해 사용할 텍스쳐의 이름으로 변경하였으니 이에 대해서는 숙제입니다. 히힛
"numverts"
이 subset에 대한 정점의 개수입니다. 정점 정의는 이 라인밑에 바로 나옵니다.
"vert"
이 문자열 뒤 라인의 내용은 정점의 정의입니다. "vert" 다음은 정수값으로 정점의 인덱스를 나타냅니다. 그 다음은 이 정점에 대한 텍스쳐 좌표입니다. (괄호 안) 그 다음 또 다른 정수값이 있는데 정점에 대한 "시작 weight"의 인덱스 또는 ID입니다. "시작 weight" 뒤에는 정점이 사용할 weight 개수입니다. 각 정점은 틀림없이 하나 이상의 weight를 가지므로 첫번째 weight의 ID가 사용되고 이 시작 weight 바로 뒤로 "n-1"개의 weight가 정점의 위치를 계산하는데 사용될 것입니다. ("n"은 이 정점에서 저장된 weight의 개수입니다)
"numtris"
여기는 subset 내 삼각형의 개수입니다. 이 뒤에 나오는 라인은 인덱스로 subset을 구성하는 삼각형입니다.
"tri"
"tri"로 시작하는 라인들은 이 subset을 구성하는 인덱스 리스트 부분입니다. "tri" 오른쪽의 정수값은 이 삼각형의 ID 또는 인덱스 값이며 그 옆 정수 3개는 이 삼각형을 구성하는 정점값의 ID 또는 인덱스입니다.
"numweights"
이 subset에 사용된 weight의 개수입니다. 다음 줄은 사용된 weight의 설명을 담고 있습니다.
"weight"
이 라인은 weight를 정의합니다. "weight" 다음 첫 값은 현재 weight의 인덱스 또는 ID값입니다. 그 다음 값은 정수로 이 weight가 묶일 관절의 ID 또는 인덱스 값을 나타냅니다. 각 weight는 한 관절에만 바인딩 될 수 있습니다. 그 다음은 "가중치" 값으로 이 weight를 사용하는 정점들에 weight가 얼마나 영향을 미치는지를 나타냅니다. 정점이 바인딩 된 모든 weight들은 반드시 "가중치"의 총합을 "1"로 되게 해야 합니다. 이 라인의 마지막 부분은 3D 벡터(괄호 안)로 "관절 공간"에서 weight 위치를 나타내는데 즉 관절 위치에 따른 weight 위치입니다. (weight의 관점에서 관절 위치를 볼때 관절 위치는 (0,0,0)이기 때문이다)
Quaternion rotations (Brief Intro.)
앞에서 말했듯이 MD5 포맷은 관절의 방향에 대해 사원수를 사용하며 weight 위치를 계산하고 궁극적으로 최종 정점 위치를 구합니다. 사원수의 수학적 배경은 꽤 복잡할 수 있지만(저도 완벽히는 모릅니다. 그 말인 즉슨 회전에 대해 사원수를 사용하는데 그 이상 필요되지 않습니다.) 쨌든 배경 아이디어는 어렵지 않습니다.
사원수는 회전에 사용되는 4D 벡터이며 회전 행렬을 대신할 수 있습니다. 뿐만 아니라 단지 4개의 요소만 사용하여(반면 동일 행렬은 16개를 사용한다) 계산 속도가 더 빠르다고 합니다. 또 짐벌락이라 부르는 현상도 피할 수 있습니다.
사원수에 대해 수학적으로 깊이 얘기하지는 않지만 특정 회전에 대해 어떻게 사용하는지를 설명하도록 노력할 것입니다.(weight를 관절 주위로 회전시켜야 하기 때문에) 사원수에 대한 많은 정의들을 찾았었지만 다 제가 찾는 것 이상으로 더 복잡해 보였습니다. 제가 얘기했듯이 사원수는 (w,x,y,z) 4개 요소를 가지며 directx는 (x,y,z,w) 순으로 저장하는 것 같습니다. (x,y,z) 요소는 회전"축"을 정의하며 그래서 만약 xyz가 (0,1,0)이라면 y축을 기준으로 회전이 이루어질 것입니다. w 요소는 사원수 회전을 동작시킵니다. w는 기본적으로 그 자체로 회전입니다. w는 0~1 사이 값이며 0은 0도 1은 360도가 됩니다.
사원수는 교환법칙이 성립하지 않습니다. 행렬처럼 곱하는 순서가 중요합다는 얘기입니다.
3D 벡터를 사원수로 바꾸기 위해 여러분이 할 것은 w요소를 "0"으로 저장하는 것입니다. 그리고 사원수에서 3D 벡터로 바꾸고 싶을때 그냥 w 요소를 무시할 수 있습니다.
관절 방향을 저장한 뒤 w 요소를 계산해야할 것입니다. 사원수로 회전을 할때 유닛 사원수(단위 사원수; 사원수의 크기가 "1")를 사용해야합니다. 유닛 사원수는 다음 방정식을 만족합니다.
마치 3D 유닛 벡터가 이것을 만족시키는 것처럼
이걸 알면 사원수 w 요소를 이렇게 계산할 수 있습니다.
이 방정식을 이용하여 점을 회전할 수 있습니다.
"-quaternionRotation"는 "quaternionRotation"의 켤레 사원수라 부르는데 "quaternionRotation"의 x, y, z부호를 반전시켜 쉽게 얻을 수 있습니다. 바로 이렇게
두 사원수를 곱하는 것은 엄청 간단하지는 않지만 우리가 항상 사용하는 xna 수학 라이브러리는 이를 위한 XMQuaternionMultiply(q1, q2) 함수를 가지고 있어 편리하게 해줍니다.
사원수에 관해 더 알고싶으시면 많은 곳이 있지만 제가 설명한 것의 더 자세한 설명을 한 여기 링크를 추천하고 싶습니다.
Calculating Vertex's Final Position
쭉 보면 MD5는 OBJ와는 매우 다른 것 같습니다. 최종 정점 위치를 계산하기 위해 먼저 관절 위치와 방향에 기인한 weight 위치를 계산해야 합니다.
가장 먼저 할일은 특정 정점이 바인딩 된 각 weight들을 확인하는 것입니다. 그리곤 관절 공간에서 weight의 최종 위치를 계산하고 관절이 위치한 객체 공간(로컬 좌표를 얘기하는 듯)으로 이동시켜야 합니다. 이 위치를 weight 가중치와 곱하고 최종 정점 위치에 더합니다. 제가 최대한 코드에서 일어나는 일을 상세히 설명했습니다. 자 이제 지금까지 간단한 인트로였고 자세히 살펴보도록 하겠습니다.
기억해보세요. 각 정점은 시작 weight의 인덱스 정수값과 사용할 weight 개수값을 저장하고 있습니다. 먼저 정점이 명시하는 weight 개수를 살펴볼 루프로 들어갑니다. 첫번째는 시작 weight가 되고 다음은 weight 인덱스 리스트의 시작 weight 다음 weight들을 따라갑니다.
이 weight가 바인딩된 관절을 찾으면 관절 방향의 켤레 사원수를 계산합니다.
그리곤 다음 방정식을 따라 점을 회전시킵니다.
이 식은 (0,0,0) 주변에 위치한 weight를 회전시키며 이때 관절 공간으로 위치시킵니다. 이제 회전된 점을 모델 공간상의 관절 위치로 이동변환을 해야합니다. 이미 회전을 했기때문에 이해하는데 어렵지 않을 것입니다. 마지막으로 최종 위치에 weight 가중치 요인을 곱하고 그 결과를 최종 정점 위치에 더합니다.
정점 위치에 영향을 주는 각 weight에 대한 루프를 보도록 하겠습니다.
Updated Vertex Structure
우리는 정점이 바인딩 되는 시작 weight 인덱스 값, weight 개수를 저장할 vertex 구조체를 업데이트 해야합니다. 또 여기서 이 두 값(weight 인덱스와 개수)는 쉐이더가 사용하지 않기 때문에 쉐이더로 보내지지 않는 것을 아셨으면 합니다. 매우 쉽습니다. 우리가 해야할 일은 쉐이더로 보내지 않는 것은 구조체의 끝에 놓고 아래에서 볼 수 있듯이 정점 레이아웃에 포함시키지 안흔 것입니다.
struct Vertex //Overloaded Vertex Structure
{
Vertex(){}
Vertex(float x, float y, float z,
float u, float v,
float nx, float ny, float nz,
float tx, float ty, float tz)
: pos(x,y,z), texCoord(u, v), normal(nx, ny, nz),
tangent(tx, ty, tz){}
XMFLOAT3 pos;
XMFLOAT2 texCoord;
XMFLOAT3 normal;
XMFLOAT3 tangent;
XMFLOAT3 biTangent;
///////////////**************new**************////////////////////
// Will not be sent to shader
int StartWeight;
int WeightCount;
///////////////**************new**************////////////////////
};
D3D11_INPUT_ELEMENT_DESC layout[] =
{
{ "POSITION", 0, DXGI_FORMAT_R32G32B32_FLOAT, 0, 0, D3D11_INPUT_PER_VERTEX_DATA, 0 },
{ "TEXCOORD", 0, DXGI_FORMAT_R32G32_FLOAT, 0, 12, D3D11_INPUT_PER_VERTEX_DATA, 0 },
{ "NORMAL", 0, DXGI_FORMAT_R32G32B32_FLOAT, 0, 20, D3D11_INPUT_PER_VERTEX_DATA, 0},
{ "TANGENT", 0, DXGI_FORMAT_R32G32B32_FLOAT, 0, 32, D3D11_INPUT_PER_VERTEX_DATA, 0}
};
UINT numElements = ARRAYSIZE(layout);
Joint Structure
어떤 것들을 쉽게 하기위해 여러 새 구조체를 가집니다. 그것은 바로 관절, weight, 모델 subsets, 모델 입니다. 첫번째로 볼 것은 관절 구조체로 md5mesh 파일로부터 앞서 얘기했던 모든 관절 정보를 저장할 것입니다.
Weight Structure
위 관절 구조체처럼 weight 구조체도 md5mesh 파일로부터 조사했던 정보를 저장할 것입니다.
The ModelSubset Structure
이 구조체는 우리의 모델의 중요한 모든 것들을 저장할 것입니다. 모델의 각 서브셋당 구조체 하나씩 가질 것입니다. 각 서브셋에 대해 새 버텍스, 인덱스 버퍼를 어떻게 만드는지 유심히 보시기 바랍니다. 그 이유는 애니메이션을 처리할 때 모델의 모든 버텍스 버퍼를 업데이트 할거 없이 서브셋의 버텍스 버퍼만 바꾸면 됩니다. 또 위치 배열도 가집니다. 충돌 체크, 픽킹( 마우스로 클릭한 오브젝트 검출) , 위치 배열이 필요한 모든것에 대해 모든 정점 배열과 기타 텍스쳐 좌표같은 것들을 쓰기보다 매우 유용할 것입니다.
The Model3D Structure
이 구조체는 모델에 적용할 모든 정보를 가질 것입니다. 그냥 훑어봐도 이해하실 거라고 믿어요.
New Globals
이번 강좌에는 전역변수가 단 2개만 있습니다. 첫번째 것은 우리의 모델을 위한(제가 만든 모델은 씬에 대해 완전 커서) 월드 행렬이고 Model3D 는 모델의 정보를 저장할 것입니다.
The LoadMD5Model() Function Prototype
여기 우리의 md5 모델을 불러오고 저장할 함수의 프로토타입이 있습니다. 첫번째 파라미터는 md5 파일 이름을 가지며 두번째는 Model3D 객체 포인터이고 세번째(OBJ 파일 로딩때 했던 것 처럼) 쉐이더 리소스 뷰의 벡터(STL) 포인터이며 마지막 네번째는 텍스쳐 파일들의 이름의 벡터(STL)로 텍스쳐가 로딩되어 있는지 아닌지 확인할 수 있습니다.
CleanUp() function
CleanUp() 함수로 가보면 각 모델의 서브셋에 대한 버텍스, 인덱스 버퍼를 해제하는 곳입니다. 루프 안을 보면 모델의 서브셋 수 만큼 돌며 매 번 해당 서브셋의 버텍스, 인덱스 버퍼를 해제합니다.
The LoadMD5Model() Function
함수를 그냥 복사하기 원하시는 분들을 위해 저는 그냥 먼저 이 함수를 파헤치기 전에 전체 함수를 보여주고 싶었습니다.
bool LoadMD5Model(std::wstring filename,
Model3D& MD5Model,
std::vector<ID3D11ShaderResourceView*>& shaderResourceViewArray,
std::vector<std::wstring> texFileNameArray)
{
std::wifstream fileIn (filename.c_str()); // Open file
std::wstring checkString; // Stores the next string from our file
if(fileIn) // Check if the file was opened
{
while(fileIn) // Loop until the end of the file is reached
{
fileIn >> checkString; // Get next string from file
if(checkString == L"MD5Version") // Get MD5 version (this function supports version 10)
{
/*fileIn >> checkString;
MessageBox(0, checkString.c_str(), //display message
L"MD5Version", MB_OK);*/
}
else if ( checkString == L"commandline" )
{
std::getline(fileIn, checkString); // Ignore the rest of this line
}
else if ( checkString == L"numJoints" )
{
fileIn >> MD5Model.numJoints; // Store number of joints
}
else if ( checkString == L"numMeshes" )
{
fileIn >> MD5Model.numSubsets; // Store number of meshes or subsets which we will call them
}
else if ( checkString == L"joints" )
{
Joint tempJoint;
fileIn >> checkString; // Skip the "{"
for(int i = 0; i < MD5Model.numJoints; i++)
{
fileIn >> tempJoint.name; // Store joints name
// Sometimes the names might contain spaces. If that is the case, we need to continue
// to read the name until we get to the closing " (quotation marks)
if(tempJoint.name[tempJoint.name.size()-1] != '"')
{
wchar_t checkChar;
bool jointNameFound = false;
while(!jointNameFound)
{
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == '"')
jointNameFound = true;
tempJoint.name += checkChar;
}
}
fileIn >> tempJoint.parentID; // Store Parent joint's ID
fileIn >> checkString; // Skip the "("
// Store position of this joint (swap y and z axis if model was made in RH Coord Sys)
fileIn >> tempJoint.pos.x >> tempJoint.pos.z >> tempJoint.pos.y;
fileIn >> checkString >> checkString; // Skip the ")" and "("
// Store orientation of this joint
fileIn >> tempJoint.orientation.x >> tempJoint.orientation.z >> tempJoint.orientation.y;
// Remove the quotation marks from joints name
tempJoint.name.erase(0, 1);
//tempJoint.name.erase(tempJoint.name.size()-1, 1);
// Compute the w axis of the quaternion (The MD5 model uses a 3D vector to describe the
// direction the bone is facing. However, we need to turn this into a quaternion, and the way
// quaternions work, is the xyz values describe the axis of rotation, while the w is a value
// between 0 and 1 which describes the angle of rotation)
float t = 1.0f - ( tempJoint.orientation.x * tempJoint.orientation.x )
- ( tempJoint.orientation.y * tempJoint.orientation.y )
- ( tempJoint.orientation.z * tempJoint.orientation.z );
if ( t < 0.0f )
{
tempJoint.orientation.w = 0.0f;
}
else
{
tempJoint.orientation.w = -sqrtf(t);
}
std::getline(fileIn, checkString); // Skip rest of this line
MD5Model.joints.push_back(tempJoint); // Store the joint into this models joint vector
}
fileIn >> checkString; // Skip the "}"
}
else if ( checkString == L"mesh")
{
ModelSubset subset;
int numVerts, numTris, numWeights;
fileIn >> checkString; // Skip the "{"
fileIn >> checkString;
while ( checkString != L"}" ) // Read until '}'
{
// In this lesson, for the sake of simplicity, we will assume a textures filename is givin here.
// Usually though, the name of a material (stored in a material library. Think back to the lesson on
// loading .obj files, where the material library was contained in the file .mtl) is givin. Let this
// be an exercise to load the material from a material library such as obj's .mtl file, instead of
// just the texture like we will do here.
if(checkString == L"shader") // Load the texture or material
{
std::wstring fileNamePath;
fileIn >> fileNamePath; // Get texture's filename
// Take spaces into account if filename or material name has a space in it
if(fileNamePath[fileNamePath.size()-1] != '"')
{
wchar_t checkChar;
bool fileNameFound = false;
while(!fileNameFound)
{
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == '"')
fileNameFound = true;
fileNamePath += checkChar;
}
}
// Remove the quotation marks from texture path
fileNamePath.erase(0, 1);
fileNamePath.erase(fileNamePath.size()-1, 1);
//check if this texture has already been loaded
bool alreadyLoaded = false;
for(int i = 0; i < texFileNameArray.size(); ++i)
{
if(fileNamePath == texFileNameArray[i])
{
alreadyLoaded = true;
subset.texArrayIndex = i;
}
}
//if the texture is not already loaded, load it now
if(!alreadyLoaded)
{
ID3D11ShaderResourceView* tempMeshSRV;
hr = D3DX11CreateShaderResourceViewFromFile( d3d11Device, fileNamePath.c_str(),
NULL, NULL, &tempMeshSRV, NULL );
if(SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
texFileNameArray.push_back(fileNamePath.c_str());
subset.texArrayIndex = shaderResourceViewArray.size();
shaderResourceViewArray.push_back(tempMeshSRV);
}
else
{
MessageBox(0, fileNamePath.c_str(), //display message
L"Could Not Open:", MB_OK);
return false;
}
}
std::getline(fileIn, checkString); // Skip rest of this line
}
else if ( checkString == L"numverts")
{
fileIn >> numVerts; // Store number of vertices
std::getline(fileIn, checkString); // Skip rest of this line
for(int i = 0; i < numVerts; i++)
{
Vertex tempVert;
fileIn >> checkString // Skip "vert # ("
>> checkString
>> checkString;
fileIn >> tempVert.texCoord.x // Store tex coords
>> tempVert.texCoord.y;
fileIn >> checkString; // Skip ")"
fileIn >> tempVert.StartWeight; // Index of first weight this vert will be weighted to
fileIn >> tempVert.WeightCount; // Number of weights for this vertex
std::getline(fileIn, checkString); // Skip rest of this line
subset.vertices.push_back(tempVert); // Push back this vertex into subsets vertex vector
}
}
else if ( checkString == L"numtris")
{
fileIn >> numTris;
subset.numTriangles = numTris;
std::getline(fileIn, checkString); // Skip rest of this line
for(int i = 0; i < numTris; i++) // Loop through each triangle
{
DWORD tempIndex;
fileIn >> checkString; // Skip "tri"
fileIn >> checkString; // Skip tri counter
for(int k = 0; k < 3; k++) // Store the 3 indices
{
fileIn >> tempIndex;
subset.indices.push_back(tempIndex);
}
std::getline(fileIn, checkString); // Skip rest of this line
}
}
else if ( checkString == L"numweights")
{
fileIn >> numWeights;
std::getline(fileIn, checkString); // Skip rest of this line
for(int i = 0; i < numWeights; i++)
{
Weight tempWeight;
fileIn >> checkString >> checkString; // Skip "weight #"
fileIn >> tempWeight.jointID; // Store weight's joint ID
fileIn >> tempWeight.bias; // Store weight's influence over a vertex
fileIn >> checkString; // Skip "("
fileIn >> tempWeight.pos.x // Store weight's pos in joint's local space
>> tempWeight.pos.z
>> tempWeight.pos.y;
std::getline(fileIn, checkString); // Skip rest of this line
subset.weights.push_back(tempWeight); // Push back tempWeight into subsets Weight array
}
}
else
std::getline(fileIn, checkString); // Skip anything else
fileIn >> checkString; // Skip "}"
}
//*** find each vertex's position using the joints and weights ***//
for ( int i = 0; i < subset.vertices.size(); ++i )
{
Vertex tempVert = subset.vertices[i];
tempVert.pos = XMFLOAT3(0, 0, 0); // Make sure the vertex's pos is cleared first
// Sum up the joints and weights information to get vertex's position
for ( int j = 0; j < tempVert.WeightCount; ++j )
{
Weight tempWeight = subset.weights[tempVert.StartWeight + j];
Joint tempJoint = MD5Model.joints[tempWeight.jointID];
// Convert joint orientation and weight pos to vectors for easier computation
// When converting a 3d vector to a quaternion, you should put 0 for "w", and
// When converting a quaternion to a 3d vector, you can just ignore the "w"
XMVECTOR tempJointOrientation = XMVectorSet(tempJoint.orientation.x, tempJoint.orientation.y, tempJoint.orientation.z, tempJoint.orientation.w);
XMVECTOR tempWeightPos = XMVectorSet(tempWeight.pos.x, tempWeight.pos.y, tempWeight.pos.z, 0.0f);
// We will need to use the conjugate of the joint orientation quaternion
// To get the conjugate of a quaternion, all you have to do is inverse the x, y, and z
XMVECTOR tempJointOrientationConjugate = XMVectorSet(-tempJoint.orientation.x, -tempJoint.orientation.y, -tempJoint.orientation.z, tempJoint.orientation.w);
// Calculate vertex position (in joint space, eg. rotate the point around (0,0,0)) for this weight using the joint orientation quaternion and its conjugate
// We can rotate a point using a quaternion with the equation "rotatedPoint = quaternion * point * quaternionConjugate"
XMFLOAT3 rotatedPoint;
XMStoreFloat3(&rotatedPoint, XMQuaternionMultiply(XMQuaternionMultiply(tempJointOrientation, tempWeightPos), tempJointOrientationConjugate));
// Now move the verices position from joint space (0,0,0) to the joints position in world space, taking the weights bias into account
// The weight bias is used because multiple weights might have an effect on the vertices final position. Each weight is attached to one joint.
tempVert.pos.x += ( tempJoint.pos.x + rotatedPoint.x ) * tempWeight.bias;
tempVert.pos.y += ( tempJoint.pos.y + rotatedPoint.y ) * tempWeight.bias;
tempVert.pos.z += ( tempJoint.pos.z + rotatedPoint.z ) * tempWeight.bias;
// Basically what has happened above, is we have taken the weights position relative to the joints position
// we then rotate the weights position (so that the weight is actually being rotated around (0, 0, 0) in world space) using
// the quaternion describing the joints rotation. We have stored this rotated point in rotatedPoint, which we then add to
// the joints position (because we rotated the weight's position around (0,0,0) in world space, and now need to translate it
// so that it appears to have been rotated around the joints position). Finally we multiply the answer with the weights bias,
// or how much control the weight has over the final vertices position. All weight's bias effecting a single vertex's position
// must add up to 1.
}
subset.positions.push_back(tempVert.pos); // Store the vertices position in the position vector instead of straight into the vertex vector
// since we can use the positions vector for certain things like collision detection or picking
// without having to work with the entire vertex structure.
}
// Put the positions into the vertices for this subset
for(int i = 0; i < subset.vertices.size(); i++)
{
subset.vertices[i].pos = subset.positions[i];
}
//*** Calculate vertex normals using normal averaging ***///
std::vector<XMFLOAT3> tempNormal;
//normalized and unnormalized normals
XMFLOAT3 unnormalized = XMFLOAT3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
//Used to get vectors (sides) from the position of the verts
float vecX, vecY, vecZ;
//Two edges of our triangle
XMVECTOR edge1 = XMVectorSet(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
XMVECTOR edge2 = XMVectorSet(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
//Compute face normals
for(int i = 0; i < subset.numTriangles; ++i)
{
//Get the vector describing one edge of our triangle (edge 0,2)
vecX = subset.vertices[subset.indices[(i*3)]].pos.x - subset.vertices[subset.indices[(i*3)+2]].pos.x;
vecY = subset.vertices[subset.indices[(i*3)]].pos.y - subset.vertices[subset.indices[(i*3)+2]].pos.y;
vecZ = subset.vertices[subset.indices[(i*3)]].pos.z - subset.vertices[subset.indices[(i*3)+2]].pos.z;
edge1 = XMVectorSet(vecX, vecY, vecZ, 0.0f); //Create our first edge
//Get the vector describing another edge of our triangle (edge 2,1)
vecX = subset.vertices[subset.indices[(i*3)+2]].pos.x - subset.vertices[subset.indices[(i*3)+1]].pos.x;
vecY = subset.vertices[subset.indices[(i*3)+2]].pos.y - subset.vertices[subset.indices[(i*3)+1]].pos.y;
vecZ = subset.vertices[subset.indices[(i*3)+2]].pos.z - subset.vertices[subset.indices[(i*3)+1]].pos.z;
edge2 = XMVectorSet(vecX, vecY, vecZ, 0.0f); //Create our second edge
//Cross multiply the two edge vectors to get the un-normalized face normal
XMStoreFloat3(&unnormalized, XMVector3Cross(edge1, edge2));
tempNormal.push_back(unnormalized);
}
//Compute vertex normals (normal Averaging)
XMVECTOR normalSum = XMVectorSet(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
int facesUsing = 0;
float tX, tY, tZ; //temp axis variables
//Go through each vertex
for(int i = 0; i < subset.vertices.size(); ++i)
{
//Check which triangles use this vertex
for(int j = 0; j < subset.numTriangles; ++j)
{
if(subset.indices[j*3] == i ||
subset.indices[(j*3)+1] == i ||
subset.indices[(j*3)+2] == i)
{
tX = XMVectorGetX(normalSum) + tempNormal[j].x;
tY = XMVectorGetY(normalSum) + tempNormal[j].y;
tZ = XMVectorGetZ(normalSum) + tempNormal[j].z;
normalSum = XMVectorSet(tX, tY, tZ, 0.0f); //If a face is using the vertex, add the unormalized face normal to the normalSum
facesUsing++;
}
}
//Get the actual normal by dividing the normalSum by the number of faces sharing the vertex
normalSum = normalSum / facesUsing;
//Normalize the normalSum vector
normalSum = XMVector3Normalize(normalSum);
//Store the normal and tangent in our current vertex
subset.vertices[i].normal.x = -XMVectorGetX(normalSum);
subset.vertices[i].normal.y = -XMVectorGetY(normalSum);
subset.vertices[i].normal.z = -XMVectorGetZ(normalSum);
//Clear normalSum, facesUsing for next vertex
normalSum = XMVectorSet(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
facesUsing = 0;
}
// Create index buffer
D3D11_BUFFER_DESC indexBufferDesc;
ZeroMemory( &indexBufferDesc, sizeof(indexBufferDesc) );
indexBufferDesc.Usage = D3D11_USAGE_DEFAULT;
indexBufferDesc.ByteWidth = sizeof(DWORD) * subset.numTriangles * 3;
indexBufferDesc.BindFlags = D3D11_BIND_INDEX_BUFFER;
indexBufferDesc.CPUAccessFlags = 0;
indexBufferDesc.MiscFlags = 0;
D3D11_SUBRESOURCE_DATA iinitData;
iinitData.pSysMem = &subset.indices[0];
d3d11Device->CreateBuffer(&indexBufferDesc, &iinitData, &subset.indexBuff);
//Create Vertex Buffer
D3D11_BUFFER_DESC vertexBufferDesc;
ZeroMemory( &vertexBufferDesc, sizeof(vertexBufferDesc) );
vertexBufferDesc.Usage = D3D11_USAGE_DYNAMIC; // We will be updating this buffer, so we must set as dynamic
vertexBufferDesc.ByteWidth = sizeof( Vertex ) * subset.vertices.size();
vertexBufferDesc.BindFlags = D3D11_BIND_VERTEX_BUFFER;
vertexBufferDesc.CPUAccessFlags = D3D11_CPU_ACCESS_WRITE; // Give CPU power to write to buffer
vertexBufferDesc.MiscFlags = 0;
D3D11_SUBRESOURCE_DATA vertexBufferData;
ZeroMemory( &vertexBufferData, sizeof(vertexBufferData) );
vertexBufferData.pSysMem = &subset.vertices[0];
hr = d3d11Device->CreateBuffer( &vertexBufferDesc, &vertexBufferData, &subset.vertBuff);
// Push back the temp subset into the models subset vector
MD5Model.subsets.push_back(subset);
}
}
}
else
{
SwapChain->SetFullscreenState(false, NULL); // Make sure we are out of fullscreen
// create message
std::wstring message = L"Could not open: ";
message += filename;
MessageBox(0, message.c_str(), // display message
L"Error", MB_OK);
return false;
}
return true;
}
Opening the File
먼저 입력 filestream을 만들고 filestream으로부터 반환된 문자열을 저장할 string을 만듭니다. 그리고는 파일이 오픈됐는지 확인합니다. 안열렸으면 메시지를 띄우고 열렸으면 EOF(end of file)에 도달할때까지 도는 루프로 들어갑니다.
Read the Header Info
filestream에서 문자열을 받아서 어떤 문자인지 확인합니다. 파일 헤더중 하나이면 그에 맞춰 정보를 저장합니다.
Reading In the Joints
문자열이 "joints"이면 뒤의 라인 수(또는 중괄호("}") 를 만날때까지)는 실제 모델의 관절인 것을 알고있습니다. 모델의 관절 수 만큼 도는 루프로 각 루프마다 관절 정보를 저장합니다. 그 정보를 임시 관절(결국 관절 벡터(stl)로 밀어 넣어질)에 저장합니다. 관절 방향 사원수의 w요소를 계산해야 하는데 아래 보시면 되고 위에 설명있으니 이해하실 수 있으실 겁니다. (원치 않으시면 이해하지 않으셔도 됩니다. (응?))
관절들 이름에 관해 설명할게 2가지 있습니다. 하나는 관절 이름에 공백이 포함되는 것입니다. 이 경우 닫는 따옴표까지 이름을 읽었는지 확실히 해야 합니다. 또 하나는 이름을 다 읽은 후 따옴표를 지워야 할 것입니다.
Reading In the Subset Specific Information
이제 서브셋 특정 정보를 읽어들이는 부분을 할 것입니다. 대부분은 위에서 설명했습니다. 쉐이더(md5 서브셋; hlsl 쉐이더와 헷갈리지 말 것)를 로딩할때 obj 모델 로더에서 했던것 처럼 똑같은 걸 하는데 먼저 텍스쳐가 로딩 되어있는지 확인하고 안되있으면 로딩합니다. 그리고는 쉐이더 리소스 뷰를 쉐이더 리소스 뷰 벡터에 해당 리소스 인덱스를 우리의 서브셋에 저장합니다.
Calculating the Vertex Position
이제 이번 강좌의 가장 흥미로운 부분에 왔습니다. 실제로 관절들의 위치와 방향을 가지고 정점 위치를 계산하는 부분입니다. 제가 주석을 제 능력껏 잘 달아 놓아서 어떤 동작인지 아실테지만 한번 더(위에서 이미 설명했지만) 여기에 설명하려 합니다.
첫번째로 할 일은 서브셋의 각 정점만큼 루프를 도는 것입니다. 서브셋의 정점을 임시 정점 변수에 저장하고 위치를 원점으로 설정합니다. 그리고는 해당 정점이 붙여진 각 weight에 대한 새로운 루프로 들어갑니다. weight를 임시 weight 변수에 저장하고 그 weight가 붙여진 관절을 임시 관절 변수에 저장합니다. 그리곤 사원수(XMVECTORS는 다 사용하지 않더라도 항상 4개의 구성요소를 가집니다.)를 생성하는데 하나는 관절 방향, 또 하나는 weight 위치(weight 위치는 3D 벡터여서 "w" 요소는 "0"으로 설정하면 됩니다.), 마지막 하나는 관절 방향의 켤레 사원수입니다.
이제 또 다른 변수를 생성하는데 3D 벡터로 weight의 최종 위치를 저장할 것입니다. 그리고는 계산을 수행하는데 "관절 공간"에서 weight의 위치를 결정합니다. 무슨 말이냐면 관절은 "모델 공간"(weight 위치는 관절 위치에 관련있지 모델 공간의 원점과는 관련없다.)상의 정확한 위치에 있지 않더라도 실제로 원점을 중심으로 회전되고 있다는 얘기입니다. (음?) 그래서 weight를 관절 공간의 관절을 중심으로 회전시켰지만 weight 위치를 모델 공간으로 변환시켜야 합니다. 이건 엄청 쉽습니다. 우리가 할 일은 관절 위치를 weight 최종 위치에 더하면 되기 때문입니다.
이 최종 최종 최종 위치를 저장하기 전에 할 일이 하나 더 있는데 해당 정점에 weight 가중치를 고려하는 것입니다. 최종 최종 최종 위치에 가중치를 곱하고 그 결과를 정점에 더하면(어차피 현재 정점은 원점) 완전 최종 위치가 됩니다.
다 이해하셨을 거라고 믿습니다. 그렇지 않다면 제 생각에 여러분의 온 신경과 집중을 코드를 따라가는데 쏟는다면 사실 상당히 간단하다는 것을(사원수 곱셈 따위의 수학적 디테일은 눈감아 주세요 찡긋) 보시게 될 것입니다.
추신: "여러분이 충분히 열심히 보면 이해할 것입니다."라고 말하는 것으로 제가 아마도 여러분의 지성을 과소평가하지 말아야 합니다.(하찮게 여겨 미안하다?) 그래서 이해하지 못한 부분이 있다면 저에게 질문을 주시면 최대한 아는내에서 돕도록 하겠습니다.
Calculating the Vertex Normal
이 섹션은 OBJ 로더에서 법선 벡터 계산했을때와 거의 판박이니 모르시겠다면 obj 로더 강좌를 확인하시기 바랍니다. 이 메소드는 또 정점에 대한 법선 매핑에 대한 tangent와 bitangent를 구하는데 사용됩니다.
Creating the Index and Vertex Buffers
우리는 드디어 MD5 로더의 마지막에 왔습니다. 모델의 각 서브셋에 대한 버텍스 인덱스 버퍼를 만들 것입니다. 이전 강좌들에서 많이 했으므로 버텍스 버퍼를 제외하고 설명이 필요없습니다. 어떻게 버텍스 버퍼를 동적 버퍼로 cpu 쓰기가 가능하도록(동적 버퍼 설정 시 CPU와 GPU가 공유하는 AGP 메모리를 사용하게 된다. 그래픽 메모리로 옮기는 과정때문에 정적 버퍼보다 빠르지는 않지만 버퍼 갱신 속도가 매우 빨라 잘 안 바뀌는 맵, 지형 보다는 자주 바뀌는 데이터에 사용) 설정하는지 주의하시기 바랍니다. 그 이유는 (다음강좌) 우리의 씬 내내 애니메이션을 하기 위해 버퍼를 갱신해주어야 하기 때문입니다. 더 자세한 것은 다음 강좌에서 더 살펴볼 것입니다.
다 끝나면 임시 서브셋 변수를 우리의 모델 객체의 서브셋 배열에 푸쉬합니다.
Calling the LoadMD5Model() Function
이제 initscene() 함수로 가보면 우리의 모델을 로딩하는 함수를 호출합니다. 제대로 로딩됐는지 확실히 하기 위해 확인하여 그렇지 않다면 false를 리턴합니다.
Updating the Models World Space Matrix
제가 만든 모델은 씬에 대해 정말 너무 커서 겁나 겁나 줄여야 합니다. 또 모델의 중심은 기본으로 우리 씬의 지면 아래 위치하고 있어 위로 조금 올려야 합니다.
Drawing the Model
여기 drawscene() 함수안에 우리의 모델을 그릴 것입니다. 각 모델 서브셋들을 돌고 해당 서브셋의 버텍스 인덱스 버퍼를 IA에 바인딩할 것입니다. 그리고는 WVP(월드 뷰 프로젝션 행렬)와 상수 버퍼 것들을 쉐이더에 보내고 마지막으로 서브셋을 그립니다. 모든 것은 이전 강좌에 다 설명되어 있습니다. (이 테크닉은 OBJ 로더 강좌에서 분명히 설명되어 있습니다.)
이게 이 강좌의 다 입니다. 이제 뼈대 구조체를 가지는 모델을 로딩할 수 있으며 우리의 모델을 움직일 준비를 마쳤습니다! (항상 그렇듯이) 어떻게든 이 강좌가 도움이 되었길 바랍니다!
Exercise:
1. material library를 생성하고 MD5 로더 함수를 material library를 사용하도록 바꾸세요.
2. 사원수와 친해지세요. 회전행렬 대신 회전에 대해 사원수를 사용하도록 해보세요.
3. 질문 남기세요!
4. 급나 좋은 날 되세요!
여기 최종 코드 입니다:
main.cpp
//Include and link appropriate libraries and headers//
#pragma comment(lib, "d3d11.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "d3dx11.lib")
#pragma comment(lib, "d3dx10.lib")
#pragma comment (lib, "D3D10_1.lib")
#pragma comment (lib, "DXGI.lib")
#pragma comment (lib, "D2D1.lib")
#pragma comment (lib, "dwrite.lib")
#pragma comment (lib, "dinput8.lib")
#pragma comment (lib, "dxguid.lib")
#include <windows.h>
#include <d3d11.h>
#include <d3dx11.h>
#include <d3dx10.h>
#include <xnamath.h>
#include <D3D10_1.h>
#include <DXGI.h>
#include <D2D1.h>
#include <sstream>
#include <dwrite.h>
#include <dinput.h>
#include <vector>
#include <fstream>
#include <istream>
//Global Declarations - Interfaces//
IDXGISwapChain* SwapChain;
ID3D11Device* d3d11Device;
ID3D11DeviceContext* d3d11DevCon;
ID3D11RenderTargetView* renderTargetView;
ID3D11DepthStencilView* depthStencilView;
ID3D11Texture2D* depthStencilBuffer;
ID3D11VertexShader* VS;
ID3D11PixelShader* PS;
ID3D11PixelShader* D2D_PS;
ID3D10Blob* D2D_PS_Buffer;
ID3D10Blob* VS_Buffer;
ID3D10Blob* PS_Buffer;
ID3D11InputLayout* vertLayout;
ID3D11Buffer* cbPerObjectBuffer;
ID3D11BlendState* d2dTransparency;
ID3D11RasterizerState* CCWcullMode;
ID3D11RasterizerState* CWcullMode;
ID3D11SamplerState* CubesTexSamplerState;
ID3D11Buffer* cbPerFrameBuffer;
ID3D10Device1 *d3d101Device;
IDXGIKeyedMutex *keyedMutex11;
IDXGIKeyedMutex *keyedMutex10;
ID2D1RenderTarget *D2DRenderTarget;
ID2D1SolidColorBrush *Brush;
ID3D11Texture2D *BackBuffer11;
ID3D11Texture2D *sharedTex11;
ID3D11Buffer *d2dVertBuffer;
ID3D11Buffer *d2dIndexBuffer;
ID3D11ShaderResourceView *d2dTexture;
IDWriteFactory *DWriteFactory;
IDWriteTextFormat *TextFormat;
IDirectInputDevice8* DIKeyboard;
IDirectInputDevice8* DIMouse;
ID3D11Buffer* sphereIndexBuffer;
ID3D11Buffer* sphereVertBuffer;
ID3D11VertexShader* SKYMAP_VS;
ID3D11PixelShader* SKYMAP_PS;
ID3D10Blob* SKYMAP_VS_Buffer;
ID3D10Blob* SKYMAP_PS_Buffer;
ID3D11ShaderResourceView* smrv;
ID3D11DepthStencilState* DSLessEqual;
ID3D11RasterizerState* RSCullNone;
ID3D11BlendState* Transparency;
//Mesh variables. Each loaded mesh will need its own set of these
ID3D11Buffer* meshVertBuff;
ID3D11Buffer* meshIndexBuff;
XMMATRIX meshWorld;
int meshSubsets = 0;
std::vector<int> meshSubsetIndexStart;
std::vector<int> meshSubsetTexture;
//Textures and material variables, used for all mesh's loaded
std::vector<ID3D11ShaderResourceView*> meshSRV;
std::vector<std::wstring> textureNameArray;
std::wstring printText;
//Global Declarations - Others//
LPCTSTR WndClassName = L"firstwindow";
HWND hwnd = NULL;
HRESULT hr;
int Width = 1920;
int Height = 1200;
DIMOUSESTATE mouseLastState;
LPDIRECTINPUT8 DirectInput;
float rotx = 0;
float rotz = 0;
float scaleX = 1.0f;
float scaleY = 1.0f;
XMMATRIX Rotationx;
XMMATRIX Rotationz;
XMMATRIX Rotationy;
XMMATRIX WVP;
XMMATRIX camView;
XMMATRIX camProjection;
XMMATRIX d2dWorld;
XMVECTOR camPosition;
XMVECTOR camTarget;
XMVECTOR camUp;
XMVECTOR DefaultForward = XMVectorSet(0.0f,0.0f,1.0f, 0.0f);
XMVECTOR DefaultRight = XMVectorSet(1.0f,0.0f,0.0f, 0.0f);
XMVECTOR camForward = XMVectorSet(0.0f,0.0f,1.0f, 0.0f);
XMVECTOR camRight = XMVectorSet(1.0f,0.0f,0.0f, 0.0f);
XMMATRIX camRotationMatrix;
float moveLeftRight = 0.0f;
float moveBackForward = 0.0f;
float camYaw = 0.0f;
float camPitch = 0.0f;
int NumSphereVertices;
int NumSphereFaces;
XMMATRIX sphereWorld;
XMMATRIX Rotation;
XMMATRIX Scale;
XMMATRIX Translation;
float rot = 0.01f;
double countsPerSecond = 0.0;
__int64 CounterStart = 0;
int frameCount = 0;
int fps = 0;
__int64 frameTimeOld = 0;
double frameTime;
//Function Prototypes//
bool InitializeDirect3d11App(HINSTANCE hInstance);
void CleanUp();
bool InitScene();
void DrawScene();
bool InitD2D_D3D101_DWrite(IDXGIAdapter1 *Adapter);
void InitD2DScreenTexture();
void UpdateScene(double time);
void UpdateCamera();
void RenderText(std::wstring text, int inInt);
void StartTimer();
double GetTime();
double GetFrameTime();
bool InitializeWindow(HINSTANCE hInstance,
int ShowWnd,
int width, int height,
bool windowed);
int messageloop();
bool InitDirectInput(HINSTANCE hInstance);
void DetectInput(double time);
void CreateSphere(int LatLines, int LongLines);
LRESULT CALLBACK WndProc(HWND hWnd,
UINT msg,
WPARAM wParam,
LPARAM lParam);
//Create effects constant buffer's structure//
struct cbPerObject
{
XMMATRIX WVP;
XMMATRIX World;
//These will be used for the pixel shader
XMFLOAT4 difColor;
BOOL hasTexture;
//Because of HLSL structure packing, we will use windows BOOL
//instead of bool because HLSL packs things into 4 bytes, and
//bool is only one byte, where BOOL is 4 bytes
BOOL hasNormMap;
};
cbPerObject cbPerObj;
//Create material structure
struct SurfaceMaterial
{
std::wstring matName;
XMFLOAT4 difColor;
int texArrayIndex;
int normMapTexArrayIndex;
bool hasNormMap;
bool hasTexture;
bool transparent;
};
std::vector<SurfaceMaterial> material;
//Define LoadObjModel function after we create surfaceMaterial structure
bool LoadObjModel(std::wstring filename, //.obj filename
ID3D11Buffer** vertBuff, //mesh vertex buffer
ID3D11Buffer** indexBuff, //mesh index buffer
std::vector<int>& subsetIndexStart, //start index of each subset
std::vector<int>& subsetMaterialArray, //index value of material for each subset
std::vector<SurfaceMaterial>& material, //vector of material structures
int& subsetCount, //Number of subsets in mesh
bool isRHCoordSys, //true if model was created in right hand coord system
bool computeNormals); //true to compute the normals, false to use the files normals
struct Light
{
Light()
{
ZeroMemory(this, sizeof(Light));
}
XMFLOAT3 pos;
float range;
XMFLOAT3 dir;
float cone;
XMFLOAT3 att;
float pad2;
XMFLOAT4 ambient;
XMFLOAT4 diffuse;
};
Light light;
struct cbPerFrame
{
Light light;
};
cbPerFrame constbuffPerFrame;
struct Vertex //Overloaded Vertex Structure
{
Vertex(){}
Vertex(float x, float y, float z,
float u, float v,
float nx, float ny, float nz,
float tx, float ty, float tz)
: pos(x,y,z), texCoord(u, v), normal(nx, ny, nz),
tangent(tx, ty, tz){}
XMFLOAT3 pos;
XMFLOAT2 texCoord;
XMFLOAT3 normal;
XMFLOAT3 tangent;
XMFLOAT3 biTangent;
///////////////**************new**************////////////////////
// Will not be sent to shader
int StartWeight;
int WeightCount;
///////////////**************new**************////////////////////
};
D3D11_INPUT_ELEMENT_DESC layout[] =
{
{ "POSITION", 0, DXGI_FORMAT_R32G32B32_FLOAT, 0, 0, D3D11_INPUT_PER_VERTEX_DATA, 0 },
{ "TEXCOORD", 0, DXGI_FORMAT_R32G32_FLOAT, 0, 12, D3D11_INPUT_PER_VERTEX_DATA, 0 },
{ "NORMAL", 0, DXGI_FORMAT_R32G32B32_FLOAT, 0, 20, D3D11_INPUT_PER_VERTEX_DATA, 0},
{ "TANGENT", 0, DXGI_FORMAT_R32G32B32_FLOAT, 0, 32, D3D11_INPUT_PER_VERTEX_DATA, 0}
};
UINT numElements = ARRAYSIZE(layout);
///////////////**************new**************////////////////////
struct Joint
{
std::wstring name;
int parentID;
XMFLOAT3 pos;
XMFLOAT4 orientation;
};
struct Weight
{
int jointID;
float bias;
XMFLOAT3 pos;
};
struct ModelSubset
{
int texArrayIndex;
int numTriangles;
std::vector<Vertex> vertices;
std::vector<DWORD> indices;
std::vector<Weight> weights;
std::vector<XMFLOAT3> positions;
ID3D11Buffer* vertBuff;
ID3D11Buffer* indexBuff;
};
struct Model3D
{
int numSubsets;
int numJoints;
std::vector<Joint> joints;
std::vector<ModelSubset> subsets;
};
XMMATRIX smilesWorld;
Model3D NewMD5Model;
//LoadMD5Model() function prototype
bool LoadMD5Model(std::wstring filename,
Model3D& MD5Model,
std::vector<ID3D11ShaderResourceView*>& shaderResourceViewArray,
std::vector<std::wstring> texFileNameArray);
///////////////**************new**************////////////////////
int WINAPI WinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance, //Main windows function
HINSTANCE hPrevInstance,
LPSTR lpCmdLine,
int nShowCmd)
{
if(!InitializeWindow(hInstance, nShowCmd, Width, Height, true))
{
MessageBox(0, L"Window Initialization - Failed",
L"Error", MB_OK);
return 0;
}
if(!InitializeDirect3d11App(hInstance)) //Initialize Direct3D
{
MessageBox(0, L"Direct3D Initialization - Failed",
L"Error", MB_OK);
return 0;
}
if(!InitScene()) //Initialize our scene
{
MessageBox(0, L"Scene Initialization - Failed",
L"Error", MB_OK);
return 0;
}
if(!InitDirectInput(hInstance))
{
MessageBox(0, L"Direct Input Initialization - Failed",
L"Error", MB_OK);
return 0;
}
messageloop();
CleanUp();
return 0;
}
bool InitializeWindow(HINSTANCE hInstance,
int ShowWnd,
int width, int height,
bool windowed)
{
typedef struct _WNDCLASS {
UINT cbSize;
UINT style;
WNDPROC lpfnWndProc;
int cbClsExtra;
int cbWndExtra;
HANDLE hInstance;
HICON hIcon;
HCURSOR hCursor;
HBRUSH hbrBackground;
LPCTSTR lpszMenuName;
LPCTSTR lpszClassName;
} WNDCLASS;
WNDCLASSEX wc;
wc.cbSize = sizeof(WNDCLASSEX);
wc.style = CS_HREDRAW | CS_VREDRAW;
wc.lpfnWndProc = WndProc;
wc.cbClsExtra = NULL;
wc.cbWndExtra = NULL;
wc.hInstance = hInstance;
wc.hIcon = LoadIcon(NULL, IDI_APPLICATION);
wc.hCursor = LoadCursor(NULL, IDC_ARROW);
wc.hbrBackground = (HBRUSH)(COLOR_WINDOW + 1);
wc.lpszMenuName = NULL;
wc.lpszClassName = WndClassName;
wc.hIconSm = LoadIcon(NULL, IDI_APPLICATION);
if (!RegisterClassEx(&wc))
{
MessageBox(NULL, L"Error registering class",
L"Error", MB_OK | MB_ICONERROR);
return 1;
}
hwnd = CreateWindowEx(
NULL,
WndClassName,
L"Lesson 4 - Begin Drawing",
WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW,
CW_USEDEFAULT, CW_USEDEFAULT,
width, height,
NULL,
NULL,
hInstance,
NULL
);
if (!hwnd)
{
MessageBox(NULL, L"Error creating window",
L"Error", MB_OK | MB_ICONERROR);
return 1;
}
ShowWindow(hwnd, ShowWnd);
UpdateWindow(hwnd);
return true;
}
bool InitializeDirect3d11App(HINSTANCE hInstance)
{
//Describe our SwapChain Buffer
DXGI_MODE_DESC bufferDesc;
ZeroMemory(&bufferDesc, sizeof(DXGI_MODE_DESC));
bufferDesc.Width = Width;
bufferDesc.Height = Height;
bufferDesc.RefreshRate.Numerator = 60;
bufferDesc.RefreshRate.Denominator = 1;
bufferDesc.Format = DXGI_FORMAT_B8G8R8A8_UNORM;
bufferDesc.ScanlineOrdering = DXGI_MODE_SCANLINE_ORDER_UNSPECIFIED;
bufferDesc.Scaling = DXGI_MODE_SCALING_UNSPECIFIED;
//Describe our SwapChain
DXGI_SWAP_CHAIN_DESC swapChainDesc;
ZeroMemory(&swapChainDesc, sizeof(DXGI_SWAP_CHAIN_DESC));
swapChainDesc.BufferDesc = bufferDesc;
swapChainDesc.SampleDesc.Count = 1;
swapChainDesc.SampleDesc.Quality = 0;
swapChainDesc.BufferUsage = DXGI_USAGE_RENDER_TARGET_OUTPUT;
swapChainDesc.BufferCount = 1;
swapChainDesc.OutputWindow = hwnd;
///////////////**************new**************////////////////////
swapChainDesc.Windowed = true;
///////////////**************new**************////////////////////
swapChainDesc.SwapEffect = DXGI_SWAP_EFFECT_DISCARD;
// Create DXGI factory to enumerate adapters///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
IDXGIFactory1 *DXGIFactory;
HRESULT hr = CreateDXGIFactory1(__uuidof(IDXGIFactory1), (void**)&DXGIFactory);
// Use the first adapter
IDXGIAdapter1 *Adapter;
hr = DXGIFactory->EnumAdapters1(0, &Adapter);
DXGIFactory->Release();
//Create our Direct3D 11 Device and SwapChain//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
hr = D3D11CreateDeviceAndSwapChain(Adapter, D3D_DRIVER_TYPE_UNKNOWN, NULL, D3D11_CREATE_DEVICE_BGRA_SUPPORT,
NULL, NULL, D3D11_SDK_VERSION, &swapChainDesc, &SwapChain, &d3d11Device, NULL, &d3d11DevCon);
//Initialize Direct2D, Direct3D 10.1, DirectWrite
InitD2D_D3D101_DWrite(Adapter);
//Release the Adapter interface
Adapter->Release();
//Create our BackBuffer and Render Target
hr = SwapChain->GetBuffer( 0, __uuidof( ID3D11Texture2D ), (void**)&BackBuffer11 );
hr = d3d11Device->CreateRenderTargetView( BackBuffer11, NULL, &renderTargetView );
//Describe our Depth/Stencil Buffer
D3D11_TEXTURE2D_DESC depthStencilDesc;
depthStencilDesc.Width = Width;
depthStencilDesc.Height = Height;
depthStencilDesc.MipLevels = 1;
depthStencilDesc.ArraySize = 1;
depthStencilDesc.Format = DXGI_FORMAT_D24_UNORM_S8_UINT;
depthStencilDesc.SampleDesc.Count = 1;
depthStencilDesc.SampleDesc.Quality = 0;
depthStencilDesc.Usage = D3D11_USAGE_DEFAULT;
depthStencilDesc.BindFlags = D3D11_BIND_DEPTH_STENCIL;
depthStencilDesc.CPUAccessFlags = 0;
depthStencilDesc.MiscFlags = 0;
//Create the Depth/Stencil View
d3d11Device->CreateTexture2D(&depthStencilDesc, NULL, &depthStencilBuffer);
d3d11Device->CreateDepthStencilView(depthStencilBuffer, NULL, &depthStencilView);
return true;
}
bool InitD2D_D3D101_DWrite(IDXGIAdapter1 *Adapter)
{
//Create our Direc3D 10.1 Device///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
hr = D3D10CreateDevice1(Adapter, D3D10_DRIVER_TYPE_HARDWARE, NULL,D3D10_CREATE_DEVICE_BGRA_SUPPORT,
D3D10_FEATURE_LEVEL_9_3, D3D10_1_SDK_VERSION, &d3d101Device );
//Create Shared Texture that Direct3D 10.1 will render on//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
D3D11_TEXTURE2D_DESC sharedTexDesc;
ZeroMemory(&sharedTexDesc, sizeof(sharedTexDesc));
sharedTexDesc.Width = Width;
sharedTexDesc.Height = Height;
sharedTexDesc.Format = DXGI_FORMAT_B8G8R8A8_UNORM;
sharedTexDesc.MipLevels = 1;
sharedTexDesc.ArraySize = 1;
sharedTexDesc.SampleDesc.Count = 1;
sharedTexDesc.Usage = D3D11_USAGE_DEFAULT;
sharedTexDesc.BindFlags = D3D11_BIND_SHADER_RESOURCE | D3D11_BIND_RENDER_TARGET;
sharedTexDesc.MiscFlags = D3D11_RESOURCE_MISC_SHARED_KEYEDMUTEX;
hr = d3d11Device->CreateTexture2D(&sharedTexDesc, NULL, &sharedTex11);
// Get the keyed mutex for the shared texture (for D3D11)///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
hr = sharedTex11->QueryInterface(__uuidof(IDXGIKeyedMutex), (void**)&keyedMutex11);
// Get the shared handle needed to open the shared texture in D3D10.1///////////////////////////////////////////////////
IDXGIResource *sharedResource10;
HANDLE sharedHandle10;
hr = sharedTex11->QueryInterface(__uuidof(IDXGIResource), (void**)&sharedResource10);
hr = sharedResource10->GetSharedHandle(&sharedHandle10);
sharedResource10->Release();
// Open the surface for the shared texture in D3D10.1///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
IDXGISurface1 *sharedSurface10;
hr = d3d101Device->OpenSharedResource(sharedHandle10, __uuidof(IDXGISurface1), (void**)(&sharedSurface10));
hr = sharedSurface10->QueryInterface(__uuidof(IDXGIKeyedMutex), (void**)&keyedMutex10);
// Create D2D factory///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
ID2D1Factory *D2DFactory;
hr = D2D1CreateFactory(D2D1_FACTORY_TYPE_SINGLE_THREADED, __uuidof(ID2D1Factory), (void**)&D2DFactory);
D2D1_RENDER_TARGET_PROPERTIES renderTargetProperties;
ZeroMemory(&renderTargetProperties, sizeof(renderTargetProperties));
renderTargetProperties.type = D2D1_RENDER_TARGET_TYPE_HARDWARE;
renderTargetProperties.pixelFormat = D2D1::PixelFormat(DXGI_FORMAT_UNKNOWN, D2D1_ALPHA_MODE_PREMULTIPLIED);
hr = D2DFactory->CreateDxgiSurfaceRenderTarget(sharedSurface10, &renderTargetProperties, &D2DRenderTarget);
sharedSurface10->Release();
D2DFactory->Release();
// Create a solid color brush to draw something with
hr = D2DRenderTarget->CreateSolidColorBrush(D2D1::ColorF(1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f), &Brush);
//DirectWrite///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
hr = DWriteCreateFactory(DWRITE_FACTORY_TYPE_SHARED, __uuidof(IDWriteFactory),
reinterpret_cast<IUnknown**>(&DWriteFactory));
hr = DWriteFactory->CreateTextFormat(
L"Script",
NULL,
DWRITE_FONT_WEIGHT_REGULAR,
DWRITE_FONT_STYLE_NORMAL,
DWRITE_FONT_STRETCH_NORMAL,
24.0f,
L"en-us",
&TextFormat
);
hr = TextFormat->SetTextAlignment(DWRITE_TEXT_ALIGNMENT_LEADING);
hr = TextFormat->SetParagraphAlignment(DWRITE_PARAGRAPH_ALIGNMENT_NEAR);
d3d101Device->IASetPrimitiveTopology(D3D10_PRIMITIVE_TOPOLOGY_POINTLIST);
return true;
}
bool InitDirectInput(HINSTANCE hInstance)
{
hr = DirectInput8Create(hInstance,
DIRECTINPUT_VERSION,
IID_IDirectInput8,
(void**)&DirectInput,
NULL);
hr = DirectInput->CreateDevice(GUID_SysKeyboard,
&DIKeyboard,
NULL);
hr = DirectInput->CreateDevice(GUID_SysMouse,
&DIMouse,
NULL);
hr = DIKeyboard->SetDataFormat(&c_dfDIKeyboard);
hr = DIKeyboard->SetCooperativeLevel(hwnd, DISCL_FOREGROUND | DISCL_NONEXCLUSIVE);
hr = DIMouse->SetDataFormat(&c_dfDIMouse);
hr = DIMouse->SetCooperativeLevel(hwnd, DISCL_EXCLUSIVE | DISCL_NOWINKEY | DISCL_FOREGROUND);
return true;
}
void UpdateCamera()
{
camRotationMatrix = XMMatrixRotationRollPitchYaw(camPitch, camYaw, 0);
camTarget = XMVector3TransformCoord(DefaultForward, camRotationMatrix );
camTarget = XMVector3Normalize(camTarget);
XMMATRIX RotateYTempMatrix;
RotateYTempMatrix = XMMatrixRotationY(camYaw);
// Walk
//camRight = XMVector3TransformCoord(DefaultRight, RotateYTempMatrix);
//camUp = XMVector3TransformCoord(camUp, RotateYTempMatrix);
//camForward = XMVector3TransformCoord(DefaultForward, RotateYTempMatrix);
// Free Cam
camRight = XMVector3TransformCoord(DefaultRight, camRotationMatrix);
camForward = XMVector3TransformCoord(DefaultForward, camRotationMatrix);
camUp = XMVector3Cross(camForward, camRight);
camPosition += moveLeftRight*camRight;
camPosition += moveBackForward*camForward;
moveLeftRight = 0.0f;
moveBackForward = 0.0f;
camTarget = camPosition + camTarget;
camView = XMMatrixLookAtLH( camPosition, camTarget, camUp );
}
void DetectInput(double time)
{
DIMOUSESTATE mouseCurrState;
BYTE keyboardState[256];
DIKeyboard->Acquire();
DIMouse->Acquire();
DIMouse->GetDeviceState(sizeof(DIMOUSESTATE), &mouseCurrState);
DIKeyboard->GetDeviceState(sizeof(keyboardState),(LPVOID)&keyboardState);
if(keyboardState[DIK_ESCAPE] & 0x80)
PostMessage(hwnd, WM_DESTROY, 0, 0);
float speed = 10.0f * time;
if(keyboardState[DIK_A] & 0x80)
{
moveLeftRight -= speed;
}
if(keyboardState[DIK_D] & 0x80)
{
moveLeftRight += speed;
}
if(keyboardState[DIK_W] & 0x80)
{
moveBackForward += speed;
}
if(keyboardState[DIK_S] & 0x80)
{
moveBackForward -= speed;
}
if((mouseCurrState.lX != mouseLastState.lX) || (mouseCurrState.lY != mouseLastState.lY))
{
camYaw += mouseLastState.lX * 0.001f;
camPitch += mouseCurrState.lY * 0.001f;
mouseLastState = mouseCurrState;
}
UpdateCamera();
return;
}
void CleanUp()
{
SwapChain->SetFullscreenState(false, NULL);
PostMessage(hwnd, WM_DESTROY, 0, 0);
//Release the COM Objects we created
SwapChain->Release();
d3d11Device->Release();
d3d11DevCon->Release();
renderTargetView->Release();
VS->Release();
PS->Release();
VS_Buffer->Release();
PS_Buffer->Release();
vertLayout->Release();
depthStencilView->Release();
depthStencilBuffer->Release();
cbPerObjectBuffer->Release();
Transparency->Release();
CCWcullMode->Release();
CWcullMode->Release();
d3d101Device->Release();
keyedMutex11->Release();
keyedMutex10->Release();
D2DRenderTarget->Release();
Brush->Release();
BackBuffer11->Release();
sharedTex11->Release();
DWriteFactory->Release();
TextFormat->Release();
d2dTexture->Release();
cbPerFrameBuffer->Release();
DIKeyboard->Unacquire();
DIMouse->Unacquire();
DirectInput->Release();
sphereIndexBuffer->Release();
sphereVertBuffer->Release();
SKYMAP_VS->Release();
SKYMAP_PS->Release();
SKYMAP_VS_Buffer->Release();
SKYMAP_PS_Buffer->Release();
smrv->Release();
DSLessEqual->Release();
RSCullNone->Release();
meshVertBuff->Release();
meshIndexBuff->Release();
///////////////**************new**************////////////////////
for(int i = 0; i < NewMD5Model.numSubsets; i++)
{
NewMD5Model.subsets[i].indexBuff->Release();
NewMD5Model.subsets[i].vertBuff->Release();
}
///////////////**************new**************////////////////////
}
///////////////**************new**************////////////////////
bool LoadMD5Model(std::wstring filename,
Model3D& MD5Model,
std::vector<ID3D11ShaderResourceView*>& shaderResourceViewArray,
std::vector<std::wstring> texFileNameArray)
{
std::wifstream fileIn (filename.c_str()); // Open file
std::wstring checkString; // Stores the next string from our file
if(fileIn) // Check if the file was opened
{
while(fileIn) // Loop until the end of the file is reached
{
fileIn >> checkString; // Get next string from file
if(checkString == L"MD5Version") // Get MD5 version (this function supports version 10)
{
/*fileIn >> checkString;
MessageBox(0, checkString.c_str(), //display message
L"MD5Version", MB_OK);*/
}
else if ( checkString == L"commandline" )
{
std::getline(fileIn, checkString); // Ignore the rest of this line
}
else if ( checkString == L"numJoints" )
{
fileIn >> MD5Model.numJoints; // Store number of joints
}
else if ( checkString == L"numMeshes" )
{
fileIn >> MD5Model.numSubsets; // Store number of meshes or subsets which we will call them
}
else if ( checkString == L"joints" )
{
Joint tempJoint;
fileIn >> checkString; // Skip the "{"
for(int i = 0; i < MD5Model.numJoints; i++)
{
fileIn >> tempJoint.name; // Store joints name
// Sometimes the names might contain spaces. If that is the case, we need to continue
// to read the name until we get to the closing " (quotation marks)
if(tempJoint.name[tempJoint.name.size()-1] != '"')
{
wchar_t checkChar;
bool jointNameFound = false;
while(!jointNameFound)
{
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == '"')
jointNameFound = true;
tempJoint.name += checkChar;
}
}
fileIn >> tempJoint.parentID; // Store Parent joint's ID
fileIn >> checkString; // Skip the "("
// Store position of this joint (swap y and z axis if model was made in RH Coord Sys)
fileIn >> tempJoint.pos.x >> tempJoint.pos.z >> tempJoint.pos.y;
fileIn >> checkString >> checkString; // Skip the ")" and "("
// Store orientation of this joint
fileIn >> tempJoint.orientation.x >> tempJoint.orientation.z >> tempJoint.orientation.y;
// Remove the quotation marks from joints name
tempJoint.name.erase(0, 1);
tempJoint.name.erase(tempJoint.name.size()-1, 1);
// Compute the w axis of the quaternion (The MD5 model uses a 3D vector to describe the
// direction the bone is facing. However, we need to turn this into a quaternion, and the way
// quaternions work, is the xyz values describe the axis of rotation, while the w is a value
// between 0 and 1 which describes the angle of rotation)
float t = 1.0f - ( tempJoint.orientation.x * tempJoint.orientation.x )
- ( tempJoint.orientation.y * tempJoint.orientation.y )
- ( tempJoint.orientation.z * tempJoint.orientation.z );
if ( t < 0.0f )
{
tempJoint.orientation.w = 0.0f;
}
else
{
tempJoint.orientation.w = -sqrtf(t);
}
std::getline(fileIn, checkString); // Skip rest of this line
MD5Model.joints.push_back(tempJoint); // Store the joint into this models joint vector
}
fileIn >> checkString; // Skip the "}"
}
else if ( checkString == L"mesh")
{
ModelSubset subset;
int numVerts, numTris, numWeights;
fileIn >> checkString; // Skip the "{"
fileIn >> checkString;
while ( checkString != L"}" ) // Read until '}'
{
// In this lesson, for the sake of simplicity, we will assume a textures filename is givin here.
// Usually though, the name of a material (stored in a material library. Think back to the lesson on
// loading .obj files, where the material library was contained in the file .mtl) is givin. Let this
// be an exercise to load the material from a material library such as obj's .mtl file, instead of
// just the texture like we will do here.
if(checkString == L"shader") // Load the texture or material
{
std::wstring fileNamePath;
fileIn >> fileNamePath; // Get texture's filename
// Take spaces into account if filename or material name has a space in it
if(fileNamePath[fileNamePath.size()-1] != '"')
{
wchar_t checkChar;
bool fileNameFound = false;
while(!fileNameFound)
{
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == '"')
fileNameFound = true;
fileNamePath += checkChar;
}
}
// Remove the quotation marks from texture path
fileNamePath.erase(0, 1);
fileNamePath.erase(fileNamePath.size()-1, 1);
//check if this texture has already been loaded
bool alreadyLoaded = false;
for(int i = 0; i < texFileNameArray.size(); ++i)
{
if(fileNamePath == texFileNameArray[i])
{
alreadyLoaded = true;
subset.texArrayIndex = i;
}
}
//if the texture is not already loaded, load it now
if(!alreadyLoaded)
{
ID3D11ShaderResourceView* tempMeshSRV;
hr = D3DX11CreateShaderResourceViewFromFile( d3d11Device, fileNamePath.c_str(),
NULL, NULL, &tempMeshSRV, NULL );
if(SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
texFileNameArray.push_back(fileNamePath.c_str());
subset.texArrayIndex = shaderResourceViewArray.size();
shaderResourceViewArray.push_back(tempMeshSRV);
}
else
{
MessageBox(0, fileNamePath.c_str(), //display message
L"Could Not Open:", MB_OK);
return false;
}
}
std::getline(fileIn, checkString); // Skip rest of this line
}
else if ( checkString == L"numverts")
{
fileIn >> numVerts; // Store number of vertices
std::getline(fileIn, checkString); // Skip rest of this line
for(int i = 0; i < numVerts; i++)
{
Vertex tempVert;
fileIn >> checkString // Skip "vert # ("
>> checkString
>> checkString;
fileIn >> tempVert.texCoord.x // Store tex coords
>> tempVert.texCoord.y;
fileIn >> checkString; // Skip ")"
fileIn >> tempVert.StartWeight; // Index of first weight this vert will be weighted to
fileIn >> tempVert.WeightCount; // Number of weights for this vertex
std::getline(fileIn, checkString); // Skip rest of this line
subset.vertices.push_back(tempVert); // Push back this vertex into subsets vertex vector
}
}
else if ( checkString == L"numtris")
{
fileIn >> numTris;
subset.numTriangles = numTris;
std::getline(fileIn, checkString); // Skip rest of this line
for(int i = 0; i < numTris; i++) // Loop through each triangle
{
DWORD tempIndex;
fileIn >> checkString; // Skip "tri"
fileIn >> checkString; // Skip tri counter
for(int k = 0; k < 3; k++) // Store the 3 indices
{
fileIn >> tempIndex;
subset.indices.push_back(tempIndex);
}
std::getline(fileIn, checkString); // Skip rest of this line
}
}
else if ( checkString == L"numweights")
{
fileIn >> numWeights;
std::getline(fileIn, checkString); // Skip rest of this line
for(int i = 0; i < numWeights; i++)
{
Weight tempWeight;
fileIn >> checkString >> checkString; // Skip "weight #"
fileIn >> tempWeight.jointID; // Store weight's joint ID
fileIn >> tempWeight.bias; // Store weight's influence over a vertex
fileIn >> checkString; // Skip "("
fileIn >> tempWeight.pos.x // Store weight's pos in joint's local space
>> tempWeight.pos.z
>> tempWeight.pos.y;
std::getline(fileIn, checkString); // Skip rest of this line
subset.weights.push_back(tempWeight); // Push back tempWeight into subsets Weight array
}
}
else
std::getline(fileIn, checkString); // Skip anything else
fileIn >> checkString; // Skip "}"
}
//*** find each vertex's position using the joints and weights ***//
for ( int i = 0; i < subset.vertices.size(); ++i )
{
Vertex tempVert = subset.vertices[i];
tempVert.pos = XMFLOAT3(0, 0, 0); // Make sure the vertex's pos is cleared first
// Sum up the joints and weights information to get vertex's position
for ( int j = 0; j < tempVert.WeightCount; ++j )
{
Weight tempWeight = subset.weights[tempVert.StartWeight + j];
Joint tempJoint = MD5Model.joints[tempWeight.jointID];
// Convert joint orientation and weight pos to vectors for easier computation
// When converting a 3d vector to a quaternion, you should put 0 for "w", and
// When converting a quaternion to a 3d vector, you can just ignore the "w"
XMVECTOR tempJointOrientation = XMVectorSet(tempJoint.orientation.x, tempJoint.orientation.y, tempJoint.orientation.z, tempJoint.orientation.w);
XMVECTOR tempWeightPos = XMVectorSet(tempWeight.pos.x, tempWeight.pos.y, tempWeight.pos.z, 0.0f);
// We will need to use the conjugate of the joint orientation quaternion
// To get the conjugate of a quaternion, all you have to do is inverse the x, y, and z
XMVECTOR tempJointOrientationConjugate = XMVectorSet(-tempJoint.orientation.x, -tempJoint.orientation.y, -tempJoint.orientation.z, tempJoint.orientation.w);
// Calculate vertex position (in joint space, eg. rotate the point around (0,0,0)) for this weight using the joint orientation quaternion and its conjugate
// We can rotate a point using a quaternion with the equation "rotatedPoint = quaternion * point * quaternionConjugate"
XMFLOAT3 rotatedPoint;
XMStoreFloat3(&rotatedPoint, XMQuaternionMultiply(XMQuaternionMultiply(tempJointOrientation, tempWeightPos), tempJointOrientationConjugate));
// Now move the verices position from joint space (0,0,0) to the joints position in world space, taking the weights bias into account
// The weight bias is used because multiple weights might have an effect on the vertices final position. Each weight is attached to one joint.
tempVert.pos.x += ( tempJoint.pos.x + rotatedPoint.x ) * tempWeight.bias;
tempVert.pos.y += ( tempJoint.pos.y + rotatedPoint.y ) * tempWeight.bias;
tempVert.pos.z += ( tempJoint.pos.z + rotatedPoint.z ) * tempWeight.bias;
// Basically what has happened above, is we have taken the weights position relative to the joints position
// we then rotate the weights position (so that the weight is actually being rotated around (0, 0, 0) in world space) using
// the quaternion describing the joints rotation. We have stored this rotated point in rotatedPoint, which we then add to
// the joints position (because we rotated the weight's position around (0,0,0) in world space, and now need to translate it
// so that it appears to have been rotated around the joints position). Finally we multiply the answer with the weights bias,
// or how much control the weight has over the final vertices position. All weight's bias effecting a single vertex's position
// must add up to 1.
}
subset.positions.push_back(tempVert.pos); // Store the vertices position in the position vector instead of straight into the vertex vector
// since we can use the positions vector for certain things like collision detection or picking
// without having to work with the entire vertex structure.
}
// Put the positions into the vertices for this subset
for(int i = 0; i < subset.vertices.size(); i++)
{
subset.vertices[i].pos = subset.positions[i];
}
//*** Calculate vertex normals using normal averaging ***///
std::vector<XMFLOAT3> tempNormal;
//normalized and unnormalized normals
XMFLOAT3 unnormalized = XMFLOAT3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
//Used to get vectors (sides) from the position of the verts
float vecX, vecY, vecZ;
//Two edges of our triangle
XMVECTOR edge1 = XMVectorSet(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
XMVECTOR edge2 = XMVectorSet(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
//Compute face normals
for(int i = 0; i < subset.numTriangles; ++i)
{
//Get the vector describing one edge of our triangle (edge 0,2)
vecX = subset.vertices[subset.indices[(i*3)]].pos.x - subset.vertices[subset.indices[(i*3)+2]].pos.x;
vecY = subset.vertices[subset.indices[(i*3)]].pos.y - subset.vertices[subset.indices[(i*3)+2]].pos.y;
vecZ = subset.vertices[subset.indices[(i*3)]].pos.z - subset.vertices[subset.indices[(i*3)+2]].pos.z;
edge1 = XMVectorSet(vecX, vecY, vecZ, 0.0f); //Create our first edge
//Get the vector describing another edge of our triangle (edge 2,1)
vecX = subset.vertices[subset.indices[(i*3)+2]].pos.x - subset.vertices[subset.indices[(i*3)+1]].pos.x;
vecY = subset.vertices[subset.indices[(i*3)+2]].pos.y - subset.vertices[subset.indices[(i*3)+1]].pos.y;
vecZ = subset.vertices[subset.indices[(i*3)+2]].pos.z - subset.vertices[subset.indices[(i*3)+1]].pos.z;
edge2 = XMVectorSet(vecX, vecY, vecZ, 0.0f); //Create our second edge
//Cross multiply the two edge vectors to get the un-normalized face normal
XMStoreFloat3(&unnormalized, XMVector3Cross(edge1, edge2));
tempNormal.push_back(unnormalized);
}
//Compute vertex normals (normal Averaging)
XMVECTOR normalSum = XMVectorSet(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
int facesUsing = 0;
float tX, tY, tZ; //temp axis variables
//Go through each vertex
for(int i = 0; i < subset.vertices.size(); ++i)
{
//Check which triangles use this vertex
for(int j = 0; j < subset.numTriangles; ++j)
{
if(subset.indices[j*3] == i ||
subset.indices[(j*3)+1] == i ||
subset.indices[(j*3)+2] == i)
{
tX = XMVectorGetX(normalSum) + tempNormal[j].x;
tY = XMVectorGetY(normalSum) + tempNormal[j].y;
tZ = XMVectorGetZ(normalSum) + tempNormal[j].z;
normalSum = XMVectorSet(tX, tY, tZ, 0.0f); //If a face is using the vertex, add the unormalized face normal to the normalSum
facesUsing++;
}
}
//Get the actual normal by dividing the normalSum by the number of faces sharing the vertex
normalSum = normalSum / facesUsing;
//Normalize the normalSum vector
normalSum = XMVector3Normalize(normalSum);
//Store the normal and tangent in our current vertex
subset.vertices[i].normal.x = -XMVectorGetX(normalSum);
subset.vertices[i].normal.y = -XMVectorGetY(normalSum);
subset.vertices[i].normal.z = -XMVectorGetZ(normalSum);
//Clear normalSum, facesUsing for next vertex
normalSum = XMVectorSet(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
facesUsing = 0;
}
// Create index buffer
D3D11_BUFFER_DESC indexBufferDesc;
ZeroMemory( &indexBufferDesc, sizeof(indexBufferDesc) );
indexBufferDesc.Usage = D3D11_USAGE_DEFAULT;
indexBufferDesc.ByteWidth = sizeof(DWORD) * subset.numTriangles * 3;
indexBufferDesc.BindFlags = D3D11_BIND_INDEX_BUFFER;
indexBufferDesc.CPUAccessFlags = 0;
indexBufferDesc.MiscFlags = 0;
D3D11_SUBRESOURCE_DATA iinitData;
iinitData.pSysMem = &subset.indices[0];
d3d11Device->CreateBuffer(&indexBufferDesc, &iinitData, &subset.indexBuff);
//Create Vertex Buffer
D3D11_BUFFER_DESC vertexBufferDesc;
ZeroMemory( &vertexBufferDesc, sizeof(vertexBufferDesc) );
vertexBufferDesc.Usage = D3D11_USAGE_DYNAMIC; // We will be updating this buffer, so we must set as dynamic
vertexBufferDesc.ByteWidth = sizeof( Vertex ) * subset.vertices.size();
vertexBufferDesc.BindFlags = D3D11_BIND_VERTEX_BUFFER;
vertexBufferDesc.CPUAccessFlags = D3D11_CPU_ACCESS_WRITE; // Give CPU power to write to buffer
vertexBufferDesc.MiscFlags = 0;
D3D11_SUBRESOURCE_DATA vertexBufferData;
ZeroMemory( &vertexBufferData, sizeof(vertexBufferData) );
vertexBufferData.pSysMem = &subset.vertices[0];
hr = d3d11Device->CreateBuffer( &vertexBufferDesc, &vertexBufferData, &subset.vertBuff);
// Push back the temp subset into the models subset vector
MD5Model.subsets.push_back(subset);
}
}
}
else
{
SwapChain->SetFullscreenState(false, NULL); // Make sure we are out of fullscreen
// create message
std::wstring message = L"Could not open: ";
message += filename;
MessageBox(0, message.c_str(), // display message
L"Error", MB_OK);
return false;
}
return true;
}
///////////////**************new**************////////////////////
bool LoadObjModel(std::wstring filename,
ID3D11Buffer** vertBuff,
ID3D11Buffer** indexBuff,
std::vector<int>& subsetIndexStart,
std::vector<int>& subsetMaterialArray,
std::vector<SurfaceMaterial>& material,
int& subsetCount,
bool isRHCoordSys,
bool computeNormals)
{
HRESULT hr = 0;
std::wifstream fileIn (filename.c_str()); //Open file
std::wstring meshMatLib; //String to hold our obj material library filename
//Arrays to store our model's information
std::vector<DWORD> indices;
std::vector<XMFLOAT3> vertPos;
std::vector<XMFLOAT3> vertNorm;
std::vector<XMFLOAT2> vertTexCoord;
std::vector<std::wstring> meshMaterials;
//Vertex definition indices
std::vector<int> vertPosIndex;
std::vector<int> vertNormIndex;
std::vector<int> vertTCIndex;
//Make sure we have a default if no tex coords or normals are defined
bool hasTexCoord = false;
bool hasNorm = false;
//Temp variables to store into vectors
std::wstring meshMaterialsTemp;
int vertPosIndexTemp;
int vertNormIndexTemp;
int vertTCIndexTemp;
wchar_t checkChar; //The variable we will use to store one char from file at a time
std::wstring face; //Holds the string containing our face vertices
int vIndex = 0; //Keep track of our vertex index count
int triangleCount = 0; //Total Triangles
int totalVerts = 0;
int meshTriangles = 0;
//Check to see if the file was opened
if (fileIn)
{
while(fileIn)
{
checkChar = fileIn.get(); //Get next char
switch (checkChar)
{
case '#':
checkChar = fileIn.get();
while(checkChar != '\n')
checkChar = fileIn.get();
break;
case 'v': //Get Vertex Descriptions
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == ' ') //v - vert position
{
float vz, vy, vx;
fileIn >> vx >> vy >> vz; //Store the next three types
if(isRHCoordSys) //If model is from an RH Coord System
vertPos.push_back(XMFLOAT3( vx, vy, vz * -1.0f)); //Invert the Z axis
else
vertPos.push_back(XMFLOAT3( vx, vy, vz));
}
if(checkChar == 't') //vt - vert tex coords
{
float vtcu, vtcv;
fileIn >> vtcu >> vtcv; //Store next two types
if(isRHCoordSys) //If model is from an RH Coord System
vertTexCoord.push_back(XMFLOAT2(vtcu, 1.0f-vtcv)); //Reverse the "v" axis
else
vertTexCoord.push_back(XMFLOAT2(vtcu, vtcv));
hasTexCoord = true; //We know the model uses texture coords
}
//Since we compute the normals later, we don't need to check for normals
//In the file, but i'll do it here anyway
if(checkChar == 'n') //vn - vert normal
{
float vnx, vny, vnz;
fileIn >> vnx >> vny >> vnz; //Store next three types
if(isRHCoordSys) //If model is from an RH Coord System
vertNorm.push_back(XMFLOAT3( vnx, vny, vnz * -1.0f )); //Invert the Z axis
else
vertNorm.push_back(XMFLOAT3( vnx, vny, vnz ));
hasNorm = true; //We know the model defines normals
}
break;
//New group (Subset)
case 'g': //g - defines a group
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == ' ')
{
subsetIndexStart.push_back(vIndex); //Start index for this subset
subsetCount++;
}
break;
//Get Face Index
case 'f': //f - defines the faces
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == ' ')
{
face = L"";
std::wstring VertDef; //Holds one vertex definition at a time
triangleCount = 0;
checkChar = fileIn.get();
while(checkChar != '\n')
{
face += checkChar; //Add the char to our face string
checkChar = fileIn.get(); //Get the next Character
if(checkChar == ' ') //If its a space...
triangleCount++; //Increase our triangle count
}
//Check for space at the end of our face string
if(face[face.length()-1] == ' ')
triangleCount--; //Each space adds to our triangle count
triangleCount -= 1; //Ever vertex in the face AFTER the first two are new faces
std::wstringstream ss(face);
if(face.length() > 0)
{
int firstVIndex, lastVIndex; //Holds the first and last vertice's index
for(int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) //First three vertices (first triangle)
{
ss >> VertDef; //Get vertex definition (vPos/vTexCoord/vNorm)
std::wstring vertPart;
int whichPart = 0; //(vPos, vTexCoord, or vNorm)
//Parse this string
for(int j = 0; j < VertDef.length(); ++j)
{
if(VertDef[j] != '/') //If there is no divider "/", add a char to our vertPart
vertPart += VertDef[j];
//If the current char is a divider "/", or its the last character in the string
if(VertDef[j] == '/' || j == VertDef.length()-1)
{
std::wistringstream wstringToInt(vertPart); //Used to convert wstring to int
if(whichPart == 0) //If vPos
{
wstringToInt >> vertPosIndexTemp;
vertPosIndexTemp -= 1; //subtract one since c++ arrays start with 0, and obj start with 1
//Check to see if the vert pos was the only thing specified
if(j == VertDef.length()-1)
{
vertNormIndexTemp = 0;
vertTCIndexTemp = 0;
}
}
else if(whichPart == 1) //If vTexCoord
{
if(vertPart != L"") //Check to see if there even is a tex coord
{
wstringToInt >> vertTCIndexTemp;
vertTCIndexTemp -= 1; //subtract one since c++ arrays start with 0, and obj start with 1
}
else //If there is no tex coord, make a default
vertTCIndexTemp = 0;
//If the cur. char is the second to last in the string, then
//there must be no normal, so set a default normal
if(j == VertDef.length()-1)
vertNormIndexTemp = 0;
}
else if(whichPart == 2) //If vNorm
{
std::wistringstream wstringToInt(vertPart);
wstringToInt >> vertNormIndexTemp;
vertNormIndexTemp -= 1; //subtract one since c++ arrays start with 0, and obj start with 1
}
vertPart = L""; //Get ready for next vertex part
whichPart++; //Move on to next vertex part
}
}
//Check to make sure there is at least one subset
if(subsetCount == 0)
{
subsetIndexStart.push_back(vIndex); //Start index for this subset
subsetCount++;
}
//Avoid duplicate vertices
bool vertAlreadyExists = false;
if(totalVerts >= 3) //Make sure we at least have one triangle to check
{
//Loop through all the vertices
for(int iCheck = 0; iCheck < totalVerts; ++iCheck)
{
//If the vertex position and texture coordinate in memory are the same
//As the vertex position and texture coordinate we just now got out
//of the obj file, we will set this faces vertex index to the vertex's
//index value in memory. This makes sure we don't create duplicate vertices
if(vertPosIndexTemp == vertPosIndex[iCheck] && !vertAlreadyExists)
{
if(vertTCIndexTemp == vertTCIndex[iCheck])
{
indices.push_back(iCheck); //Set index for this vertex
vertAlreadyExists = true; //If we've made it here, the vertex already exists
}
}
}
}
//If this vertex is not already in our vertex arrays, put it there
if(!vertAlreadyExists)
{
vertPosIndex.push_back(vertPosIndexTemp);
vertTCIndex.push_back(vertTCIndexTemp);
vertNormIndex.push_back(vertNormIndexTemp);
totalVerts++; //We created a new vertex
indices.push_back(totalVerts-1); //Set index for this vertex
}
//If this is the very first vertex in the face, we need to
//make sure the rest of the triangles use this vertex
if(i == 0)
{
firstVIndex = indices[vIndex]; //The first vertex index of this FACE
}
//If this was the last vertex in the first triangle, we will make sure
//the next triangle uses this one (eg. tri1(1,2,3) tri2(1,3,4) tri3(1,4,5))
if(i == 2)
{
lastVIndex = indices[vIndex]; //The last vertex index of this TRIANGLE
}
vIndex++; //Increment index count
}
meshTriangles++; //One triangle down
//If there are more than three vertices in the face definition, we need to make sure
//we convert the face to triangles. We created our first triangle above, now we will
//create a new triangle for every new vertex in the face, using the very first vertex
//of the face, and the last vertex from the triangle before the current triangle
for(int l = 0; l < triangleCount-1; ++l) //Loop through the next vertices to create new triangles
{
//First vertex of this triangle (the very first vertex of the face too)
indices.push_back(firstVIndex); //Set index for this vertex
vIndex++;
//Second Vertex of this triangle (the last vertex used in the tri before this one)
indices.push_back(lastVIndex); //Set index for this vertex
vIndex++;
//Get the third vertex for this triangle
ss >> VertDef;
std::wstring vertPart;
int whichPart = 0;
//Parse this string (same as above)
for(int j = 0; j < VertDef.length(); ++j)
{
if(VertDef[j] != '/')
vertPart += VertDef[j];
if(VertDef[j] == '/' || j == VertDef.length()-1)
{
std::wistringstream wstringToInt(vertPart);
if(whichPart == 0)
{
wstringToInt >> vertPosIndexTemp;
vertPosIndexTemp -= 1;
//Check to see if the vert pos was the only thing specified
if(j == VertDef.length()-1)
{
vertTCIndexTemp = 0;
vertNormIndexTemp = 0;
}
}
else if(whichPart == 1)
{
if(vertPart != L"")
{
wstringToInt >> vertTCIndexTemp;
vertTCIndexTemp -= 1;
}
else
vertTCIndexTemp = 0;
if(j == VertDef.length()-1)
vertNormIndexTemp = 0;
}
else if(whichPart == 2)
{
std::wistringstream wstringToInt(vertPart);
wstringToInt >> vertNormIndexTemp;
vertNormIndexTemp -= 1;
}
vertPart = L"";
whichPart++;
}
}
//Check for duplicate vertices
bool vertAlreadyExists = false;
if(totalVerts >= 3) //Make sure we at least have one triangle to check
{
for(int iCheck = 0; iCheck < totalVerts; ++iCheck)
{
if(vertPosIndexTemp == vertPosIndex[iCheck] && !vertAlreadyExists)
{
if(vertTCIndexTemp == vertTCIndex[iCheck])
{
indices.push_back(iCheck); //Set index for this vertex
vertAlreadyExists = true; //If we've made it here, the vertex already exists
}
}
}
}
if(!vertAlreadyExists)
{
vertPosIndex.push_back(vertPosIndexTemp);
vertTCIndex.push_back(vertTCIndexTemp);
vertNormIndex.push_back(vertNormIndexTemp);
totalVerts++; //New vertex created, add to total verts
indices.push_back(totalVerts-1); //Set index for this vertex
}
//Set the second vertex for the next triangle to the last vertex we got
lastVIndex = indices[vIndex]; //The last vertex index of this TRIANGLE
meshTriangles++; //New triangle defined
vIndex++;
}
}
}
break;
case 'm': //mtllib - material library filename
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == 't')
{
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == 'l')
{
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == 'l')
{
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == 'i')
{
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == 'b')
{
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == ' ')
{
//Store the material libraries file name
fileIn >> meshMatLib;
}
}
}
}
}
}
break;
case 'u': //usemtl - which material to use
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == 's')
{
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == 'e')
{
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == 'm')
{
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == 't')
{
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == 'l')
{
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == ' ')
{
meshMaterialsTemp = L""; //Make sure this is cleared
fileIn >> meshMaterialsTemp; //Get next type (string)
meshMaterials.push_back(meshMaterialsTemp);
}
}
}
}
}
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
else //If we could not open the file
{
SwapChain->SetFullscreenState(false, NULL); //Make sure we are out of fullscreen
//create message
std::wstring message = L"Could not open: ";
message += filename;
MessageBox(0, message.c_str(), //display message
L"Error", MB_OK);
return false;
}
subsetIndexStart.push_back(vIndex); //There won't be another index start after our last subset, so set it here
//sometimes "g" is defined at the very top of the file, then again before the first group of faces.
//This makes sure the first subset does not conatain "0" indices.
if(subsetIndexStart[1] == 0)
{
subsetIndexStart.erase(subsetIndexStart.begin()+1);
meshSubsets--;
}
//Make sure we have a default for the tex coord and normal
//if one or both are not specified
if(!hasNorm)
vertNorm.push_back(XMFLOAT3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f));
if(!hasTexCoord)
vertTexCoord.push_back(XMFLOAT2(0.0f, 0.0f));
//Close the obj file, and open the mtl file
fileIn.close();
fileIn.open(meshMatLib.c_str());
std::wstring lastStringRead;
int matCount = material.size(); //total materials
//kdset - If our diffuse color was not set, we can use the ambient color (which is usually the same)
//If the diffuse color WAS set, then we don't need to set our diffuse color to ambient
bool kdset = false;
if (fileIn)
{
while(fileIn)
{
checkChar = fileIn.get(); //Get next char
switch (checkChar)
{
//Check for comment
case '#':
checkChar = fileIn.get();
while(checkChar != '\n')
checkChar = fileIn.get();
break;
//Set diffuse color
case 'K':
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == 'd') //Diffuse Color
{
checkChar = fileIn.get(); //remove space
fileIn >> material[matCount-1].difColor.x;
fileIn >> material[matCount-1].difColor.y;
fileIn >> material[matCount-1].difColor.z;
kdset = true;
}
//Ambient Color (We'll store it in diffuse if there isn't a diffuse already)
if(checkChar == 'a')
{
checkChar = fileIn.get(); //remove space
if(!kdset)
{
fileIn >> material[matCount-1].difColor.x;
fileIn >> material[matCount-1].difColor.y;
fileIn >> material[matCount-1].difColor.z;
}
}
break;
//Check for transparency
case 'T':
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == 'r')
{
checkChar = fileIn.get(); //remove space
float Transparency;
fileIn >> Transparency;
material[matCount-1].difColor.w = Transparency;
if(Transparency > 0.0f)
material[matCount-1].transparent = true;
}
break;
//Some obj files specify d for transparency
case 'd':
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == ' ')
{
float Transparency;
fileIn >> Transparency;
//'d' - 0 being most transparent, and 1 being opaque, opposite of Tr
Transparency = 1.0f - Transparency;
material[matCount-1].difColor.w = Transparency;
if(Transparency > 0.0f)
material[matCount-1].transparent = true;
}
break;
//Get the diffuse map (texture)
case 'm':
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == 'a')
{
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == 'p')
{
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == '_')
{
//map_Kd - Diffuse map
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == 'K')
{
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == 'd')
{
std::wstring fileNamePath;
fileIn.get(); //Remove whitespace between map_Kd and file
//Get the file path - We read the pathname char by char since
//pathnames can sometimes contain spaces, so we will read until
//we find the file extension
bool texFilePathEnd = false;
while(!texFilePathEnd)
{
checkChar = fileIn.get();
fileNamePath += checkChar;
if(checkChar == '.')
{
for(int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
fileNamePath += fileIn.get();
texFilePathEnd = true;
}
}
//check if this texture has already been loaded
bool alreadyLoaded = false;
for(int i = 0; i < textureNameArray.size(); ++i)
{
if(fileNamePath == textureNameArray[i])
{
alreadyLoaded = true;
material[matCount-1].texArrayIndex = i;
material[matCount-1].hasTexture = true;
}
}
//if the texture is not already loaded, load it now
if(!alreadyLoaded)
{
ID3D11ShaderResourceView* tempMeshSRV;
hr = D3DX11CreateShaderResourceViewFromFile( d3d11Device, fileNamePath.c_str(),
NULL, NULL, &tempMeshSRV, NULL );
if(SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
textureNameArray.push_back(fileNamePath.c_str());
material[matCount-1].texArrayIndex = meshSRV.size();
meshSRV.push_back(tempMeshSRV);
material[matCount-1].hasTexture = true;
}
}
}
}
//map_d - alpha map
else if(checkChar == 'd')
{
//Alpha maps are usually the same as the diffuse map
//So we will assume that for now by only enabling
//transparency for this material, as we will already
//be using the alpha channel in the diffuse map
material[matCount-1].transparent = true;
}
//map_bump - bump map (we're usinga normal map though)
else if(checkChar == 'b')
{
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == 'u')
{
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == 'm')
{
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == 'p')
{
std::wstring fileNamePath;
fileIn.get(); //Remove whitespace between map_bump and file
//Get the file path - We read the pathname char by char since
//pathnames can sometimes contain spaces, so we will read until
//we find the file extension
bool texFilePathEnd = false;
while(!texFilePathEnd)
{
checkChar = fileIn.get();
fileNamePath += checkChar;
if(checkChar == '.')
{
for(int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
fileNamePath += fileIn.get();
texFilePathEnd = true;
}
}
//check if this texture has already been loaded
bool alreadyLoaded = false;
for(int i = 0; i < textureNameArray.size(); ++i)
{
if(fileNamePath == textureNameArray[i])
{
alreadyLoaded = true;
material[matCount-1].normMapTexArrayIndex = i;
material[matCount-1].hasNormMap = true;
}
}
//if the texture is not already loaded, load it now
if(!alreadyLoaded)
{
ID3D11ShaderResourceView* tempMeshSRV;
hr = D3DX11CreateShaderResourceViewFromFile( d3d11Device, fileNamePath.c_str(),
NULL, NULL, &tempMeshSRV, NULL );
if(SUCCEEDED(hr))
{
textureNameArray.push_back(fileNamePath.c_str());
material[matCount-1].normMapTexArrayIndex = meshSRV.size();
meshSRV.push_back(tempMeshSRV);
material[matCount-1].hasNormMap = true;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
break;
case 'n': //newmtl - Declare new material
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == 'e')
{
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == 'w')
{
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == 'm')
{
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == 't')
{
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == 'l')
{
checkChar = fileIn.get();
if(checkChar == ' ')
{
//New material, set its defaults
SurfaceMaterial tempMat;
material.push_back(tempMat);
fileIn >> material[matCount].matName;
material[matCount].transparent = false;
material[matCount].hasTexture = false;
material[matCount].hasNormMap = false;
material[matCount].normMapTexArrayIndex = 0;
material[matCount].texArrayIndex = 0;
matCount++;
kdset = false;
}
}
}
}
}
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
else
{
SwapChain->SetFullscreenState(false, NULL); //Make sure we are out of fullscreen
std::wstring message = L"Could not open: ";
message += meshMatLib;
MessageBox(0, message.c_str(),
L"Error", MB_OK);
return false;
}
//Set the subsets material to the index value
//of the its material in our material array
for(int i = 0; i < meshSubsets; ++i)
{
bool hasMat = false;
for(int j = 0; j < material.size(); ++j)
{
if(meshMaterials[i] == material[j].matName)
{
subsetMaterialArray.push_back(j);
hasMat = true;
}
}
if(!hasMat)
subsetMaterialArray.push_back(0); //Use first material in array
}
std::vector<Vertex> vertices;
Vertex tempVert;
//Create our vertices using the information we got
//from the file and store them in a vector
for(int j = 0 ; j < totalVerts; ++j)
{
tempVert.pos = vertPos[vertPosIndex[j]];
tempVert.normal = vertNorm[vertNormIndex[j]];
tempVert.texCoord = vertTexCoord[vertTCIndex[j]];
vertices.push_back(tempVert);
}
//////////////////////Compute Normals///////////////////////////
//If computeNormals was set to true then we will create our own
//normals, if it was set to false we will use the obj files normals
if(computeNormals)
{
std::vector<XMFLOAT3> tempNormal;
//normalized and unnormalized normals
XMFLOAT3 unnormalized = XMFLOAT3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
//tangent stuff
std::vector<XMFLOAT3> tempTangent;
XMFLOAT3 tangent = XMFLOAT3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
float tcU1, tcV1, tcU2, tcV2;
//Used to get vectors (sides) from the position of the verts
float vecX, vecY, vecZ;
//Two edges of our triangle
XMVECTOR edge1 = XMVectorSet(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
XMVECTOR edge2 = XMVectorSet(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
//Compute face normals
//And Tangents
for(int i = 0; i < meshTriangles; ++i)
{
//Get the vector describing one edge of our triangle (edge 0,2)
vecX = vertices[indices[(i*3)]].pos.x - vertices[indices[(i*3)+2]].pos.x;
vecY = vertices[indices[(i*3)]].pos.y - vertices[indices[(i*3)+2]].pos.y;
vecZ = vertices[indices[(i*3)]].pos.z - vertices[indices[(i*3)+2]].pos.z;
edge1 = XMVectorSet(vecX, vecY, vecZ, 0.0f); //Create our first edge
//Get the vector describing another edge of our triangle (edge 2,1)
vecX = vertices[indices[(i*3)+2]].pos.x - vertices[indices[(i*3)+1]].pos.x;
vecY = vertices[indices[(i*3)+2]].pos.y - vertices[indices[(i*3)+1]].pos.y;
vecZ = vertices[indices[(i*3)+2]].pos.z - vertices[indices[(i*3)+1]].pos.z;
edge2 = XMVectorSet(vecX, vecY, vecZ, 0.0f); //Create our second edge
//Cross multiply the two edge vectors to get the un-normalized face normal
XMStoreFloat3(&unnormalized, XMVector3Cross(edge1, edge2));
tempNormal.push_back(unnormalized);
//Find first texture coordinate edge 2d vector
tcU1 = vertices[indices[(i*3)]].texCoord.x - vertices[indices[(i*3)+2]].texCoord.x;
tcV1 = vertices[indices[(i*3)]].texCoord.y - vertices[indices[(i*3)+2]].texCoord.y;
//Find second texture coordinate edge 2d vector
tcU2 = vertices[indices[(i*3)+2]].texCoord.x - vertices[indices[(i*3)+1]].texCoord.x;
tcV2 = vertices[indices[(i*3)+2]].texCoord.y - vertices[indices[(i*3)+1]].texCoord.y;
//Find tangent using both tex coord edges and position edges
tangent.x = (tcV1 * XMVectorGetX(edge1) - tcV2 * XMVectorGetX(edge2)) * (1.0f / (tcU1 * tcV2 - tcU2 * tcV1));
tangent.y = (tcV1 * XMVectorGetY(edge1) - tcV2 * XMVectorGetY(edge2)) * (1.0f / (tcU1 * tcV2 - tcU2 * tcV1));
tangent.z = (tcV1 * XMVectorGetZ(edge1) - tcV2 * XMVectorGetZ(edge2)) * (1.0f / (tcU1 * tcV2 - tcU2 * tcV1));
tempTangent.push_back(tangent);
}
//Compute vertex normals (normal Averaging)
XMVECTOR normalSum = XMVectorSet(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
XMVECTOR tangentSum = XMVectorSet(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
int facesUsing = 0;
float tX, tY, tZ; //temp axis variables
//Go through each vertex
for(int i = 0; i < totalVerts; ++i)
{
//Check which triangles use this vertex
for(int j = 0; j < meshTriangles; ++j)
{
if(indices[j*3] == i ||
indices[(j*3)+1] == i ||
indices[(j*3)+2] == i)
{
tX = XMVectorGetX(normalSum) + tempNormal[j].x;
tY = XMVectorGetY(normalSum) + tempNormal[j].y;
tZ = XMVectorGetZ(normalSum) + tempNormal[j].z;
normalSum = XMVectorSet(tX, tY, tZ, 0.0f); //If a face is using the vertex, add the unormalized face normal to the normalSum
//We can reuse tX, tY, tZ to sum up tangents
tX = XMVectorGetX(tangentSum) + tempTangent[j].x;
tY = XMVectorGetY(tangentSum) + tempTangent[j].y;
tZ = XMVectorGetZ(tangentSum) + tempTangent[j].z;
tangentSum = XMVectorSet(tX, tY, tZ, 0.0f); //sum up face tangents using this vertex
facesUsing++;
}
}
//Get the actual normal by dividing the normalSum by the number of faces sharing the vertex
normalSum = normalSum / facesUsing;
tangentSum = tangentSum / facesUsing;
//Normalize the normalSum vector and tangent
normalSum = XMVector3Normalize(normalSum);
tangentSum = XMVector3Normalize(tangentSum);
//Store the normal and tangent in our current vertex
vertices[i].normal.x = XMVectorGetX(normalSum);
vertices[i].normal.y = XMVectorGetY(normalSum);
vertices[i].normal.z = XMVectorGetZ(normalSum);
vertices[i].tangent.x = XMVectorGetX(tangentSum);
vertices[i].tangent.y = XMVectorGetY(tangentSum);
vertices[i].tangent.z = XMVectorGetZ(tangentSum);
//Clear normalSum, tangentSum and facesUsing for next vertex
normalSum = XMVectorSet(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
tangentSum = XMVectorSet(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
facesUsing = 0;
}
}
//Create index buffer
D3D11_BUFFER_DESC indexBufferDesc;
ZeroMemory( &indexBufferDesc, sizeof(indexBufferDesc) );
indexBufferDesc.Usage = D3D11_USAGE_DEFAULT;
indexBufferDesc.ByteWidth = sizeof(DWORD) * meshTriangles*3;
indexBufferDesc.BindFlags = D3D11_BIND_INDEX_BUFFER;
indexBufferDesc.CPUAccessFlags = 0;
indexBufferDesc.MiscFlags = 0;
D3D11_SUBRESOURCE_DATA iinitData;
iinitData.pSysMem = &indices[0];
d3d11Device->CreateBuffer(&indexBufferDesc, &iinitData, indexBuff);
//Create Vertex Buffer
D3D11_BUFFER_DESC vertexBufferDesc;
ZeroMemory( &vertexBufferDesc, sizeof(vertexBufferDesc) );
vertexBufferDesc.Usage = D3D11_USAGE_DEFAULT;
vertexBufferDesc.ByteWidth = sizeof( Vertex ) * totalVerts;
vertexBufferDesc.BindFlags = D3D11_BIND_VERTEX_BUFFER;
vertexBufferDesc.CPUAccessFlags = 0;
vertexBufferDesc.MiscFlags = 0;
D3D11_SUBRESOURCE_DATA vertexBufferData;
ZeroMemory( &vertexBufferData, sizeof(vertexBufferData) );
vertexBufferData.pSysMem = &vertices[0];
hr = d3d11Device->CreateBuffer( &vertexBufferDesc, &vertexBufferData, vertBuff);
return true;
}
void CreateSphere(int LatLines, int LongLines)
{
NumSphereVertices = ((LatLines-2) * LongLines) + 2;
NumSphereFaces = ((LatLines-3)*(LongLines)*2) + (LongLines*2);
float sphereYaw = 0.0f;
float spherePitch = 0.0f;
std::vector<Vertex> vertices(NumSphereVertices);
XMVECTOR currVertPos = XMVectorSet(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
vertices[0].pos.x = 0.0f;
vertices[0].pos.y = 0.0f;
vertices[0].pos.z = 1.0f;
for(DWORD i = 0; i < LatLines-2; ++i)
{
spherePitch = (i+1) * (3.14f/(LatLines-1));
Rotationx = XMMatrixRotationX(spherePitch);
for(DWORD j = 0; j < LongLines; ++j)
{
sphereYaw = j * (6.28f/(LongLines));
Rotationy = XMMatrixRotationZ(sphereYaw);
currVertPos = XMVector3TransformNormal( XMVectorSet(0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f), (Rotationx * Rotationy) );
currVertPos = XMVector3Normalize( currVertPos );
vertices[i*LongLines+j+1].pos.x = XMVectorGetX(currVertPos);
vertices[i*LongLines+j+1].pos.y = XMVectorGetY(currVertPos);
vertices[i*LongLines+j+1].pos.z = XMVectorGetZ(currVertPos);
}
}
vertices[NumSphereVertices-1].pos.x = 0.0f;
vertices[NumSphereVertices-1].pos.y = 0.0f;
vertices[NumSphereVertices-1].pos.z = -1.0f;
D3D11_BUFFER_DESC vertexBufferDesc;
ZeroMemory( &vertexBufferDesc, sizeof(vertexBufferDesc) );
vertexBufferDesc.Usage = D3D11_USAGE_DEFAULT;
vertexBufferDesc.ByteWidth = sizeof( Vertex ) * NumSphereVertices;
vertexBufferDesc.BindFlags = D3D11_BIND_VERTEX_BUFFER;
vertexBufferDesc.CPUAccessFlags = 0;
vertexBufferDesc.MiscFlags = 0;
D3D11_SUBRESOURCE_DATA vertexBufferData;
ZeroMemory( &vertexBufferData, sizeof(vertexBufferData) );
vertexBufferData.pSysMem = &vertices[0];
hr = d3d11Device->CreateBuffer( &vertexBufferDesc, &vertexBufferData, &sphereVertBuffer);
std::vector<DWORD> indices(NumSphereFaces * 3);
int k = 0;
for(DWORD l = 0; l < LongLines-1; ++l)
{
indices[k] = 0;
indices[k+1] = l+1;
indices[k+2] = l+2;
k += 3;
}
indices[k] = 0;
indices[k+1] = LongLines;
indices[k+2] = 1;
k += 3;
for(DWORD i = 0; i < LatLines-3; ++i)
{
for(DWORD j = 0; j < LongLines-1; ++j)
{
indices[k] = i*LongLines+j+1;
indices[k+1] = i*LongLines+j+2;
indices[k+2] = (i+1)*LongLines+j+1;
indices[k+3] = (i+1)*LongLines+j+1;
indices[k+4] = i*LongLines+j+2;
indices[k+5] = (i+1)*LongLines+j+2;
k += 6; // next quad
}
indices[k] = (i*LongLines)+LongLines;
indices[k+1] = (i*LongLines)+1;
indices[k+2] = ((i+1)*LongLines)+LongLines;
indices[k+3] = ((i+1)*LongLines)+LongLines;
indices[k+4] = (i*LongLines)+1;
indices[k+5] = ((i+1)*LongLines)+1;
k += 6;
}
for(DWORD l = 0; l < LongLines-1; ++l)
{
indices[k] = NumSphereVertices-1;
indices[k+1] = (NumSphereVertices-1)-(l+1);
indices[k+2] = (NumSphereVertices-1)-(l+2);
k += 3;
}
indices[k] = NumSphereVertices-1;
indices[k+1] = (NumSphereVertices-1)-LongLines;
indices[k+2] = NumSphereVertices-2;
D3D11_BUFFER_DESC indexBufferDesc;
ZeroMemory( &indexBufferDesc, sizeof(indexBufferDesc) );
indexBufferDesc.Usage = D3D11_USAGE_DEFAULT;
indexBufferDesc.ByteWidth = sizeof(DWORD) * NumSphereFaces * 3;
indexBufferDesc.BindFlags = D3D11_BIND_INDEX_BUFFER;
indexBufferDesc.CPUAccessFlags = 0;
indexBufferDesc.MiscFlags = 0;
D3D11_SUBRESOURCE_DATA iinitData;
iinitData.pSysMem = &indices[0];
d3d11Device->CreateBuffer(&indexBufferDesc, &iinitData, &sphereIndexBuffer);
}
void InitD2DScreenTexture()
{
//Create the vertex buffer
Vertex v[] =
{
// Front Face
Vertex(-1.0f, -1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f,-1.0f, -1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f),
Vertex(-1.0f, 1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,-1.0f, 1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f),
Vertex( 1.0f, 1.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f),
Vertex( 1.0f, -1.0f, -1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, -1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f),
};
DWORD indices[] = {
// Front Face
0, 1, 2,
0, 2, 3,
};
D3D11_BUFFER_DESC indexBufferDesc;
ZeroMemory( &indexBufferDesc, sizeof(indexBufferDesc) );
indexBufferDesc.Usage = D3D11_USAGE_DEFAULT;
indexBufferDesc.ByteWidth = sizeof(DWORD) * 2 * 3;
indexBufferDesc.BindFlags = D3D11_BIND_INDEX_BUFFER;
indexBufferDesc.CPUAccessFlags = 0;
indexBufferDesc.MiscFlags = 0;
D3D11_SUBRESOURCE_DATA iinitData;
iinitData.pSysMem = indices;
d3d11Device->CreateBuffer(&indexBufferDesc, &iinitData, &d2dIndexBuffer);
D3D11_BUFFER_DESC vertexBufferDesc;
ZeroMemory( &vertexBufferDesc, sizeof(vertexBufferDesc) );
vertexBufferDesc.Usage = D3D11_USAGE_DEFAULT;
vertexBufferDesc.ByteWidth = sizeof( Vertex ) * 4;
vertexBufferDesc.BindFlags = D3D11_BIND_VERTEX_BUFFER;
vertexBufferDesc.CPUAccessFlags = 0;
vertexBufferDesc.MiscFlags = 0;
D3D11_SUBRESOURCE_DATA vertexBufferData;
ZeroMemory( &vertexBufferData, sizeof(vertexBufferData) );
vertexBufferData.pSysMem = v;
hr = d3d11Device->CreateBuffer( &vertexBufferDesc, &vertexBufferData, &d2dVertBuffer);
//Create A shader resource view from the texture D2D will render to,
//So we can use it to texture a square which overlays our scene
d3d11Device->CreateShaderResourceView(sharedTex11, NULL, &d2dTexture);
}
bool InitScene()
{
InitD2DScreenTexture();
CreateSphere(10, 10);
if(!LoadObjModel(L"ground.obj", &meshVertBuff, &meshIndexBuff, meshSubsetIndexStart, meshSubsetTexture, material, meshSubsets, true, true))
return false;
///////////////**************new**************////////////////////
if(!LoadMD5Model(L"boy.md5mesh", NewMD5Model, meshSRV, textureNameArray))
return false;
///////////////**************new**************////////////////////
//Compile Shaders from shader file
hr = D3DX11CompileFromFile(L"Effects.fx", 0, 0, "VS", "vs_4_0", 0, 0, 0, &VS_Buffer, 0, 0);
hr = D3DX11CompileFromFile(L"Effects.fx", 0, 0, "PS", "ps_4_0", 0, 0, 0, &PS_Buffer, 0, 0);
hr = D3DX11CompileFromFile(L"Effects.fx", 0, 0, "D2D_PS", "ps_4_0", 0, 0, 0, &D2D_PS_Buffer, 0, 0);
hr = D3DX11CompileFromFile(L"Effects.fx", 0, 0, "SKYMAP_VS", "vs_4_0", 0, 0, 0, &SKYMAP_VS_Buffer, 0, 0);
hr = D3DX11CompileFromFile(L"Effects.fx", 0, 0, "SKYMAP_PS", "ps_4_0", 0, 0, 0, &SKYMAP_PS_Buffer, 0, 0);
//Create the Shader Objects
hr = d3d11Device->CreateVertexShader(VS_Buffer->GetBufferPointer(), VS_Buffer->GetBufferSize(), NULL, &VS);
hr = d3d11Device->CreatePixelShader(PS_Buffer->GetBufferPointer(), PS_Buffer->GetBufferSize(), NULL, &PS);
hr = d3d11Device->CreatePixelShader(D2D_PS_Buffer->GetBufferPointer(), D2D_PS_Buffer->GetBufferSize(), NULL, &D2D_PS);
hr = d3d11Device->CreateVertexShader(SKYMAP_VS_Buffer->GetBufferPointer(), SKYMAP_VS_Buffer->GetBufferSize(), NULL, &SKYMAP_VS);
hr = d3d11Device->CreatePixelShader(SKYMAP_PS_Buffer->GetBufferPointer(), SKYMAP_PS_Buffer->GetBufferSize(), NULL, &SKYMAP_PS);
//Set Vertex and Pixel Shaders
d3d11DevCon->VSSetShader(VS, 0, 0);
d3d11DevCon->PSSetShader(PS, 0, 0);
light.pos = XMFLOAT3(0.0f, 7.0f, 0.0f);
light.dir = XMFLOAT3(-0.5f, 0.75f, -0.5f);
light.range = 1000.0f;
light.cone = 12.0f;
light.att = XMFLOAT3(0.4f, 0.02f, 0.000f);
light.ambient = XMFLOAT4(0.2f, 0.2f, 0.2f, 1.0f);
light.diffuse = XMFLOAT4(1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
//Create the Input Layout
hr = d3d11Device->CreateInputLayout( layout, numElements, VS_Buffer->GetBufferPointer(),
VS_Buffer->GetBufferSize(), &vertLayout );
//Set the Input Layout
d3d11DevCon->IASetInputLayout( vertLayout );
//Set Primitive Topology
d3d11DevCon->IASetPrimitiveTopology( D3D11_PRIMITIVE_TOPOLOGY_TRIANGLELIST );
//Create the Viewport
D3D11_VIEWPORT viewport;
ZeroMemory(&viewport, sizeof(D3D11_VIEWPORT));
viewport.TopLeftX = 0;
viewport.TopLeftY = 0;
viewport.Width = Width;
viewport.Height = Height;
viewport.MinDepth = 0.0f;
viewport.MaxDepth = 1.0f;
//Set the Viewport
d3d11DevCon->RSSetViewports(1, &viewport);
//Create the buffer to send to the cbuffer in effect file
D3D11_BUFFER_DESC cbbd;
ZeroMemory(&cbbd, sizeof(D3D11_BUFFER_DESC));
cbbd.Usage = D3D11_USAGE_DEFAULT;
cbbd.ByteWidth = sizeof(cbPerObject);
cbbd.BindFlags = D3D11_BIND_CONSTANT_BUFFER;
cbbd.CPUAccessFlags = 0;
cbbd.MiscFlags = 0;
hr = d3d11Device->CreateBuffer(&cbbd, NULL, &cbPerObjectBuffer);
//Create the buffer to send to the cbuffer per frame in effect file
ZeroMemory(&cbbd, sizeof(D3D11_BUFFER_DESC));
cbbd.Usage = D3D11_USAGE_DEFAULT;
cbbd.ByteWidth = sizeof(cbPerFrame);
cbbd.BindFlags = D3D11_BIND_CONSTANT_BUFFER;
cbbd.CPUAccessFlags = 0;
cbbd.MiscFlags = 0;
hr = d3d11Device->CreateBuffer(&cbbd, NULL, &cbPerFrameBuffer);
//Camera information
camPosition = XMVectorSet( 0.0f, 5.0f, -8.0f, 0.0f );
camTarget = XMVectorSet( 0.0f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f );
camUp = XMVectorSet( 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f );
//Set the View matrix
camView = XMMatrixLookAtLH( camPosition, camTarget, camUp );
//Set the Projection matrix
camProjection = XMMatrixPerspectiveFovLH( 0.4f*3.14f, (float)Width/Height, 1.0f, 1000.0f);
D3D11_BLEND_DESC blendDesc;
ZeroMemory( &blendDesc, sizeof(blendDesc) );
D3D11_RENDER_TARGET_BLEND_DESC rtbd;
ZeroMemory( &rtbd, sizeof(rtbd) );
rtbd.BlendEnable = true;
rtbd.SrcBlend = D3D11_BLEND_SRC_COLOR;
rtbd.DestBlend = D3D11_BLEND_INV_SRC_ALPHA;
rtbd.BlendOp = D3D11_BLEND_OP_ADD;
rtbd.SrcBlendAlpha = D3D11_BLEND_ONE;
rtbd.DestBlendAlpha = D3D11_BLEND_ZERO;
rtbd.BlendOpAlpha = D3D11_BLEND_OP_ADD;
rtbd.RenderTargetWriteMask = D3D10_COLOR_WRITE_ENABLE_ALL;
blendDesc.AlphaToCoverageEnable = false;
blendDesc.RenderTarget[0] = rtbd;
d3d11Device->CreateBlendState(&blendDesc, &d2dTransparency);
ZeroMemory( &rtbd, sizeof(rtbd) );
rtbd.BlendEnable = true;
rtbd.SrcBlend = D3D11_BLEND_INV_SRC_ALPHA;
rtbd.DestBlend = D3D11_BLEND_SRC_ALPHA;
rtbd.BlendOp = D3D11_BLEND_OP_ADD;
rtbd.SrcBlendAlpha = D3D11_BLEND_INV_SRC_ALPHA;
rtbd.DestBlendAlpha = D3D11_BLEND_SRC_ALPHA;
rtbd.BlendOpAlpha = D3D11_BLEND_OP_ADD;
rtbd.RenderTargetWriteMask = D3D10_COLOR_WRITE_ENABLE_ALL;
blendDesc.AlphaToCoverageEnable = false;
blendDesc.RenderTarget[0] = rtbd;
d3d11Device->CreateBlendState(&blendDesc, &Transparency);
///Load Skymap's cube texture///
D3DX11_IMAGE_LOAD_INFO loadSMInfo;
loadSMInfo.MiscFlags = D3D11_RESOURCE_MISC_TEXTURECUBE;
ID3D11Texture2D* SMTexture = 0;
hr = D3DX11CreateTextureFromFile(d3d11Device, L"skymap.dds",
&loadSMInfo, 0, (ID3D11Resource**)&SMTexture, 0);
D3D11_TEXTURE2D_DESC SMTextureDesc;
SMTexture->GetDesc(&SMTextureDesc);
D3D11_SHADER_RESOURCE_VIEW_DESC SMViewDesc;
SMViewDesc.Format = SMTextureDesc.Format;
SMViewDesc.ViewDimension = D3D11_SRV_DIMENSION_TEXTURECUBE;
SMViewDesc.TextureCube.MipLevels = SMTextureDesc.MipLevels;
SMViewDesc.TextureCube.MostDetailedMip = 0;
hr = d3d11Device->CreateShaderResourceView(SMTexture, &SMViewDesc, &smrv);
// Describe the Sample State
D3D11_SAMPLER_DESC sampDesc;
ZeroMemory( &sampDesc, sizeof(sampDesc) );
sampDesc.Filter = D3D11_FILTER_MIN_MAG_MIP_LINEAR;
sampDesc.AddressU = D3D11_TEXTURE_ADDRESS_WRAP;
sampDesc.AddressV = D3D11_TEXTURE_ADDRESS_WRAP;
sampDesc.AddressW = D3D11_TEXTURE_ADDRESS_WRAP;
sampDesc.ComparisonFunc = D3D11_COMPARISON_NEVER;
sampDesc.MinLOD = 0;
sampDesc.MaxLOD = D3D11_FLOAT32_MAX;
//Create the Sample State
hr = d3d11Device->CreateSamplerState( &sampDesc, &CubesTexSamplerState );
D3D11_RASTERIZER_DESC cmdesc;
ZeroMemory(&cmdesc, sizeof(D3D11_RASTERIZER_DESC));
cmdesc.FillMode = D3D11_FILL_SOLID;
cmdesc.CullMode = D3D11_CULL_BACK;
cmdesc.FrontCounterClockwise = true;
hr = d3d11Device->CreateRasterizerState(&cmdesc, &CCWcullMode);
cmdesc.FrontCounterClockwise = false;
hr = d3d11Device->CreateRasterizerState(&cmdesc, &CWcullMode);
cmdesc.CullMode = D3D11_CULL_NONE;
//cmdesc.FillMode = D3D11_FILL_WIREFRAME;
hr = d3d11Device->CreateRasterizerState(&cmdesc, &RSCullNone);
D3D11_DEPTH_STENCIL_DESC dssDesc;
ZeroMemory(&dssDesc, sizeof(D3D11_DEPTH_STENCIL_DESC));
dssDesc.DepthEnable = true;
dssDesc.DepthWriteMask = D3D11_DEPTH_WRITE_MASK_ALL;
dssDesc.DepthFunc = D3D11_COMPARISON_LESS_EQUAL;
d3d11Device->CreateDepthStencilState(&dssDesc, &DSLessEqual);
return true;
}
void StartTimer()
{
LARGE_INTEGER frequencyCount;
QueryPerformanceFrequency(&frequencyCount);
countsPerSecond = double(frequencyCount.QuadPart);
QueryPerformanceCounter(&frequencyCount);
CounterStart = frequencyCount.QuadPart;
}
double GetTime()
{
LARGE_INTEGER currentTime;
QueryPerformanceCounter(¤tTime);
return double(currentTime.QuadPart-CounterStart)/countsPerSecond;
}
double GetFrameTime()
{
LARGE_INTEGER currentTime;
__int64 tickCount;
QueryPerformanceCounter(¤tTime);
tickCount = currentTime.QuadPart-frameTimeOld;
frameTimeOld = currentTime.QuadPart;
if(tickCount < 0.0f)
tickCount = 0.0f;
return float(tickCount)/countsPerSecond;
}
void UpdateScene(double time)
{
//Reset sphereWorld
sphereWorld = XMMatrixIdentity();
//Define sphereWorld's world space matrix
Scale = XMMatrixScaling( 5.0f, 5.0f, 5.0f );
//Make sure the sphere is always centered around camera
Translation = XMMatrixTranslation( XMVectorGetX(camPosition), XMVectorGetY(camPosition), XMVectorGetZ(camPosition) );
//Set sphereWorld's world space using the transformations
sphereWorld = Scale * Translation;
//the loaded models world space
meshWorld = XMMatrixIdentity();
Rotation = XMMatrixRotationY(3.14f);
Scale = XMMatrixScaling( 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f );
Translation = XMMatrixTranslation( 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f );
meshWorld = Rotation * Scale * Translation;
///////////////**************new**************////////////////////
Scale = XMMatrixScaling( 0.04f, 0.04f, 0.04f ); // The model is a bit too large for our scene, so make it smaller
Translation = XMMatrixTranslation( 0.0f, 3.0f, 0.0f );
smilesWorld = Scale * Translation;
///////////////**************new**************////////////////////
}
void RenderText(std::wstring text, int inInt)
{
d3d11DevCon->PSSetShader(D2D_PS, 0, 0);
//Release the D3D 11 Device
keyedMutex11->ReleaseSync(0);
//Use D3D10.1 device
keyedMutex10->AcquireSync(0, 5);
//Draw D2D content
D2DRenderTarget->BeginDraw();
//Clear D2D Background
D2DRenderTarget->Clear(D2D1::ColorF(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f));
//Create our string
std::wostringstream printString;
printString << text << inInt;
printText = printString.str();
//Set the Font Color
D2D1_COLOR_F FontColor = D2D1::ColorF(1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
//Set the brush color D2D will use to draw with
Brush->SetColor(FontColor);
//Create the D2D Render Area
D2D1_RECT_F layoutRect = D2D1::RectF(0, 0, Width, Height);
//Draw the Text
D2DRenderTarget->DrawText(
printText.c_str(),
wcslen(printText.c_str()),
TextFormat,
layoutRect,
Brush
);
D2DRenderTarget->EndDraw();
//Release the D3D10.1 Device
keyedMutex10->ReleaseSync(1);
//Use the D3D11 Device
keyedMutex11->AcquireSync(1, 5);
//Use the shader resource representing the direct2d render target
//to texture a square which is rendered in screen space so it
//overlays on top of our entire scene. We use alpha blending so
//that the entire background of the D2D render target is "invisible",
//And only the stuff we draw with D2D will be visible (the text)
//Set the blend state for D2D render target texture objects
d3d11DevCon->OMSetBlendState(d2dTransparency, NULL, 0xffffffff);
//Set the d2d Index buffer
d3d11DevCon->IASetIndexBuffer( d2dIndexBuffer, DXGI_FORMAT_R32_UINT, 0);
//Set the d2d vertex buffer
UINT stride = sizeof( Vertex );
UINT offset = 0;
d3d11DevCon->IASetVertexBuffers( 0, 1, &d2dVertBuffer, &stride, &offset );
WVP = XMMatrixIdentity();
cbPerObj.WVP = XMMatrixTranspose(WVP);
d3d11DevCon->UpdateSubresource( cbPerObjectBuffer, 0, NULL, &cbPerObj, 0, 0 );
d3d11DevCon->VSSetConstantBuffers( 0, 1, &cbPerObjectBuffer );
d3d11DevCon->PSSetShaderResources( 0, 1, &d2dTexture );
d3d11DevCon->PSSetSamplers( 0, 1, &CubesTexSamplerState );
d3d11DevCon->RSSetState(CWcullMode);
d3d11DevCon->DrawIndexed( 6, 0, 0 );
}
void DrawScene()
{
//Clear our render target and depth/stencil view
float bgColor[4] = { 0.1f, 0.1f, 0.1f, 1.0f };
d3d11DevCon->ClearRenderTargetView(renderTargetView, bgColor);
d3d11DevCon->ClearDepthStencilView(depthStencilView, D3D11_CLEAR_DEPTH|D3D11_CLEAR_STENCIL, 1.0f, 0);
constbuffPerFrame.light = light;
d3d11DevCon->UpdateSubresource( cbPerFrameBuffer, 0, NULL, &constbuffPerFrame, 0, 0 );
d3d11DevCon->PSSetConstantBuffers(0, 1, &cbPerFrameBuffer);
//Set our Render Target
d3d11DevCon->OMSetRenderTargets( 1, &renderTargetView, depthStencilView );
//Set the default blend state (no blending) for opaque objects
d3d11DevCon->OMSetBlendState(0, 0, 0xffffffff);
//Set Vertex and Pixel Shaders
d3d11DevCon->VSSetShader(VS, 0, 0);
d3d11DevCon->PSSetShader(PS, 0, 0);
UINT stride = sizeof( Vertex );
UINT offset = 0;
///////////////**************new**************////////////////////
///***Draw MD5 Model***///
for(int i = 0; i < NewMD5Model.numSubsets; i ++)
{
//Set the grounds index buffer
d3d11DevCon->IASetIndexBuffer( NewMD5Model.subsets[i].indexBuff, DXGI_FORMAT_R32_UINT, 0);
//Set the grounds vertex buffer
d3d11DevCon->IASetVertexBuffers( 0, 1, &NewMD5Model.subsets[i].vertBuff, &stride, &offset );
//Set the WVP matrix and send it to the constant buffer in effect file
WVP = smilesWorld * camView * camProjection;
cbPerObj.WVP = XMMatrixTranspose(WVP);
cbPerObj.World = XMMatrixTranspose(smilesWorld);
cbPerObj.hasTexture = true; // We'll assume all md5 subsets have textures
cbPerObj.hasNormMap = false; // We'll also assume md5 models have no normal map (easy to change later though)
d3d11DevCon->UpdateSubresource( cbPerObjectBuffer, 0, NULL, &cbPerObj, 0, 0 );
d3d11DevCon->VSSetConstantBuffers( 0, 1, &cbPerObjectBuffer );
d3d11DevCon->PSSetConstantBuffers( 1, 1, &cbPerObjectBuffer );
d3d11DevCon->PSSetShaderResources( 0, 1, &meshSRV[NewMD5Model.subsets[i].texArrayIndex] );
d3d11DevCon->PSSetSamplers( 0, 1, &CubesTexSamplerState );
d3d11DevCon->RSSetState(RSCullNone);
d3d11DevCon->DrawIndexed( NewMD5Model.subsets[i].indices.size(), 0, 0 );
}
///////////////**************new**************////////////////////
/////Draw our model's NON-transparent subsets/////
for(int i = 0; i < meshSubsets; ++i)
{
//Set the grounds index buffer
d3d11DevCon->IASetIndexBuffer( meshIndexBuff, DXGI_FORMAT_R32_UINT, 0);
//Set the grounds vertex buffer
d3d11DevCon->IASetVertexBuffers( 0, 1, &meshVertBuff, &stride, &offset );
//Set the WVP matrix and send it to the constant buffer in effect file
WVP = meshWorld * camView * camProjection;
cbPerObj.WVP = XMMatrixTranspose(WVP);
cbPerObj.World = XMMatrixTranspose(meshWorld);
cbPerObj.difColor = material[meshSubsetTexture[i]].difColor;
cbPerObj.hasTexture = material[meshSubsetTexture[i]].hasTexture;
cbPerObj.hasNormMap = material[meshSubsetTexture[i]].hasNormMap;
d3d11DevCon->UpdateSubresource( cbPerObjectBuffer, 0, NULL, &cbPerObj, 0, 0 );
d3d11DevCon->VSSetConstantBuffers( 0, 1, &cbPerObjectBuffer );
d3d11DevCon->PSSetConstantBuffers( 1, 1, &cbPerObjectBuffer );
if(material[meshSubsetTexture[i]].hasTexture)
d3d11DevCon->PSSetShaderResources( 0, 1, &meshSRV[material[meshSubsetTexture[i]].texArrayIndex] );
if(material[meshSubsetTexture[i]].hasNormMap)
d3d11DevCon->PSSetShaderResources( 1, 1, &meshSRV[material[meshSubsetTexture[i]].normMapTexArrayIndex] );
d3d11DevCon->PSSetSamplers( 0, 1, &CubesTexSamplerState );
d3d11DevCon->RSSetState(RSCullNone);
int indexStart = meshSubsetIndexStart[i];
int indexDrawAmount = meshSubsetIndexStart[i+1] - meshSubsetIndexStart[i];
if(!material[meshSubsetTexture[i]].transparent)
d3d11DevCon->DrawIndexed( indexDrawAmount, indexStart, 0 );
}
/////Draw the Sky's Sphere//////
//Set the spheres index buffer
d3d11DevCon->IASetIndexBuffer( sphereIndexBuffer, DXGI_FORMAT_R32_UINT, 0);
//Set the spheres vertex buffer
d3d11DevCon->IASetVertexBuffers( 0, 1, &sphereVertBuffer, &stride, &offset );
//Set the WVP matrix and send it to the constant buffer in effect file
WVP = sphereWorld * camView * camProjection;
cbPerObj.WVP = XMMatrixTranspose(WVP);
cbPerObj.World = XMMatrixTranspose(sphereWorld);
d3d11DevCon->UpdateSubresource( cbPerObjectBuffer, 0, NULL, &cbPerObj, 0, 0 );
d3d11DevCon->VSSetConstantBuffers( 0, 1, &cbPerObjectBuffer );
//Send our skymap resource view to pixel shader
d3d11DevCon->PSSetShaderResources( 0, 1, &smrv );
d3d11DevCon->PSSetSamplers( 0, 1, &CubesTexSamplerState );
//Set the new VS and PS shaders
d3d11DevCon->VSSetShader(SKYMAP_VS, 0, 0);
d3d11DevCon->PSSetShader(SKYMAP_PS, 0, 0);
//Set the new depth/stencil and RS states
d3d11DevCon->OMSetDepthStencilState(DSLessEqual, 0);
d3d11DevCon->RSSetState(RSCullNone);
d3d11DevCon->DrawIndexed( NumSphereFaces * 3, 0, 0 );
//Set the default VS, PS shaders and depth/stencil state
d3d11DevCon->VSSetShader(VS, 0, 0);
d3d11DevCon->PSSetShader(PS, 0, 0);
d3d11DevCon->OMSetDepthStencilState(NULL, 0);
/////Draw our model's TRANSPARENT subsets now/////
//Set our blend state
d3d11DevCon->OMSetBlendState(Transparency, NULL, 0xffffffff);
for(int i = 0; i < meshSubsets; ++i)
{
//Set the grounds index buffer
d3d11DevCon->IASetIndexBuffer( meshIndexBuff, DXGI_FORMAT_R32_UINT, 0);
//Set the grounds vertex buffer
d3d11DevCon->IASetVertexBuffers( 0, 1, &meshVertBuff, &stride, &offset );
//Set the WVP matrix and send it to the constant buffer in effect file
WVP = meshWorld * camView * camProjection;
cbPerObj.WVP = XMMatrixTranspose(WVP);
cbPerObj.World = XMMatrixTranspose(meshWorld);
cbPerObj.difColor = material[meshSubsetTexture[i]].difColor;
cbPerObj.hasTexture = material[meshSubsetTexture[i]].hasTexture;
cbPerObj.hasNormMap = material[meshSubsetTexture[i]].hasNormMap;
d3d11DevCon->UpdateSubresource( cbPerObjectBuffer, 0, NULL, &cbPerObj, 0, 0 );
d3d11DevCon->VSSetConstantBuffers( 0, 1, &cbPerObjectBuffer );
d3d11DevCon->PSSetConstantBuffers( 1, 1, &cbPerObjectBuffer );
if(material[meshSubsetTexture[i]].hasTexture)
d3d11DevCon->PSSetShaderResources( 0, 1, &meshSRV[material[meshSubsetTexture[i]].texArrayIndex] );
if(material[meshSubsetTexture[i]].hasNormMap)
d3d11DevCon->PSSetShaderResources( 1, 1, &meshSRV[material[meshSubsetTexture[i]].normMapTexArrayIndex] );
d3d11DevCon->PSSetSamplers( 0, 1, &CubesTexSamplerState );
d3d11DevCon->RSSetState(RSCullNone);
int indexStart = meshSubsetIndexStart[i];
int indexDrawAmount = meshSubsetIndexStart[i+1] - meshSubsetIndexStart[i];
if(material[meshSubsetTexture[i]].transparent)
d3d11DevCon->DrawIndexed( indexDrawAmount, indexStart, 0 );
}
RenderText(L"FPS: ", fps);
//Present the backbuffer to the screen
SwapChain->Present(0, 0);
}
int messageloop(){
MSG msg;
ZeroMemory(&msg, sizeof(MSG));
while(true)
{
BOOL PeekMessageL(
LPMSG lpMsg,
HWND hWnd,
UINT wMsgFilterMin,
UINT wMsgFilterMax,
UINT wRemoveMsg
);
if (PeekMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0, PM_REMOVE))
{
if (msg.message == WM_QUIT)
break;
TranslateMessage(&msg);
DispatchMessage(&msg);
}
else{
// run game code
frameCount++;
if(GetTime() > 1.0f)
{
fps = frameCount;
frameCount = 0;
StartTimer();
}
frameTime = GetFrameTime();
DetectInput(frameTime);
UpdateScene(frameTime);
DrawScene();
}
}
return msg.wParam;
}
LRESULT CALLBACK WndProc(HWND hwnd,
UINT msg,
WPARAM wParam,
LPARAM lParam)
{
switch( msg )
{
case WM_KEYDOWN:
if( wParam == VK_ESCAPE ){
DestroyWindow(hwnd);
}
return 0;
case WM_DESTROY:
PostQuitMessage(0);
return 0;
}
return DefWindowProc(hwnd,
msg,
wParam,
lParam);
}
Effects.fx









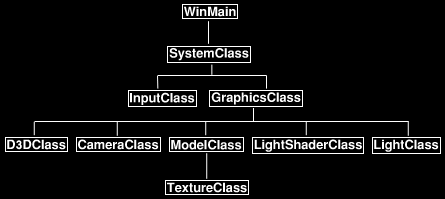



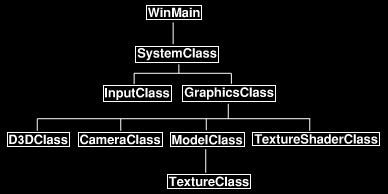

 dx11src05.zip
dx11src05.zip


